简介
DFRobot新推BMP388气压传感器,具有温度检测和大气压检测双重功能。支持Arduino代码控制,相对于旧版的BMP180,BMP280,BMP388拥有更低的功耗,更高的分辨率以及更高的采样频率。
气压传感器通常用于大气压检测和温度检测,并且由于气压和海拔高度之间的关系,人们通常可以利用气压来检测海拔高度和相对的楼层高度。在导航方面,气压计也可以用来增强GPS定位效果或者配合IMU传感器,实现三维(3D)室内导航。
BMP388基于博世成熟的压电式压力传感器技术,具有高EMC稳健性,高精度,低功耗等特点。精度约为±8Pa,相当于高度误差为±0.66 m,支持0~65℃温度检测。
注意:由于传感器对环境条件非常敏感,请勿用手指触摸。
应用领域
- 温度检测
- 大气压强检测
- 海拔高度检测
- 室内导航(楼层检测、电梯检测)
- 户外导航、休闲和运动的应用程序
- 医疗保健应用程序(如肺活量测定法)
- 垂直速度指示(如上升/下沉速度)
技术规格
- 工作电压:3.3V-5.5V
- 工作电流:0.5mA
- 测量范围:300-1250 hPa
- 相对气压测量精度:±0.08 hPa(等价±0.66m @700-900hPa,25℃-40℃)
- 绝对气压测量精度:±0.5 hPa(0℃-65℃@300-1100hPa)
- 温度漂移系数:±0.75 Pa/K(-20℃-65℃@700-1100hPa)
- 绝对温度测量精度:±0.5℃(@0℃-65℃)
- 工作温度:-40℃~80℃(在0℃-65℃测量更精确)
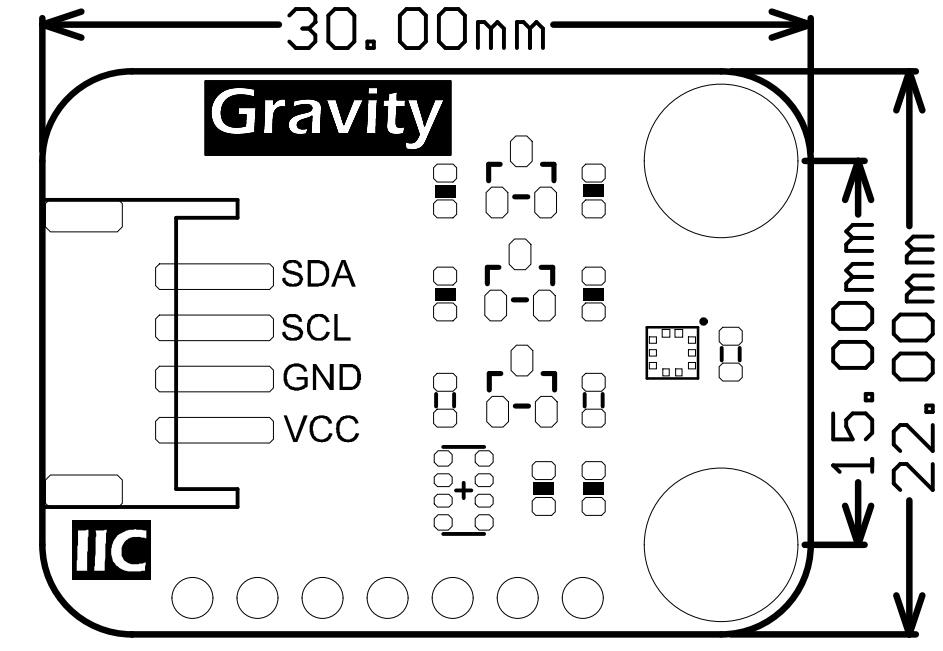
- 外形尺寸:22mm x 30mm
- 安装孔位置:15mm
- 安装孔尺寸:内径3mm/外径6mm
- 接口:Gravity-I2C 4Pin或者SPI(SPI仅在3.3V电压下使用)
引脚说明

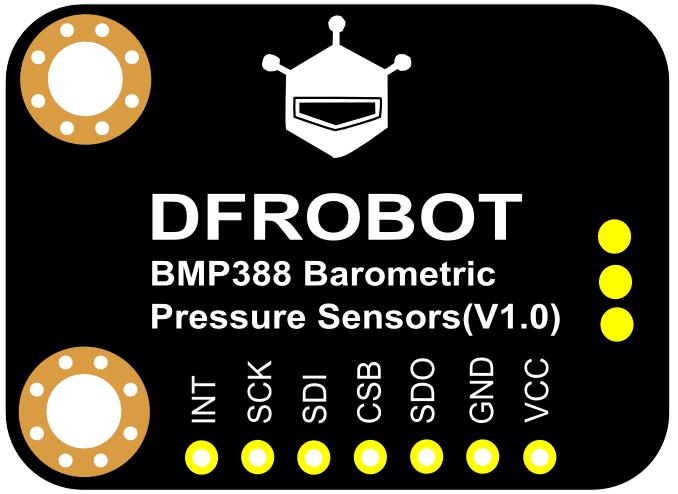
| 丝印 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| SDA | I2C数据 |
| SCL | I2C时钟 |
| INT | 中断输出引脚 |
| SCK | SPI-CLK |
| SDI | SPI-MOSI |
| CSB | SPI-CS |
| SDO | SPI-MISO/I2C地址选择 |
| GND | 电源负极 |
| VCC | 电源正极 |
使用教程
- 目标:测出当前环境下的大气压强和温度值,计算出模块当前所在环境的海拔高度
准备
- 硬件
- 1 x Arduino UNO控制板
- 1 x Gravity I2C BMP388 温度&气压计
- 若干 杜邦线
- 软件
- Arduino IDE 点击下载Arduino IDE
接线图
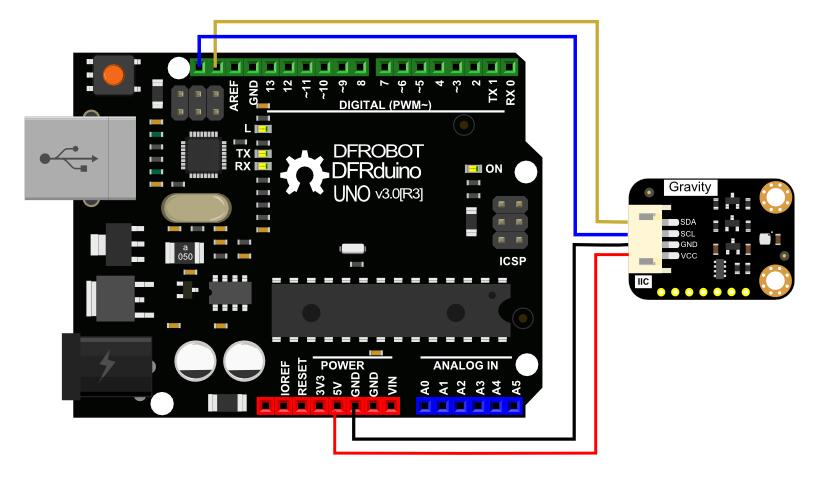
连接模块与UNO主板(通过I2C接口),按照如下图的方式连接。
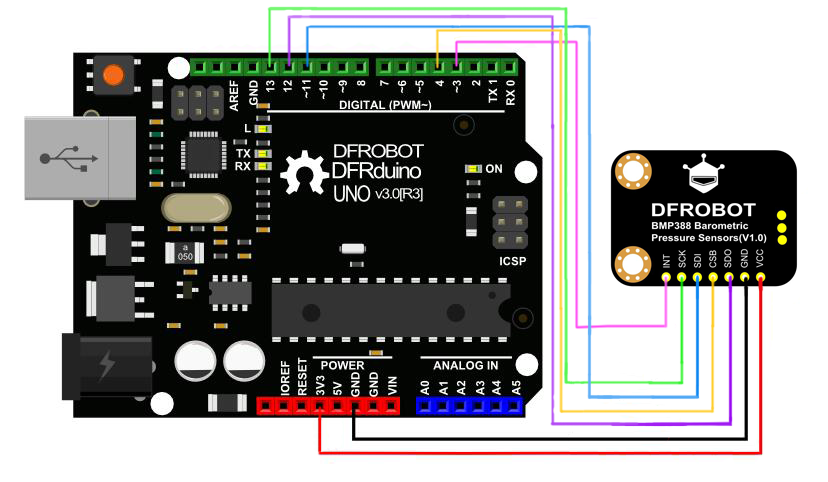
连接模块与UNO主板(通过SPI接口),按照如下图的方式连接(csPin可设置为任意数字引脚)。
样例代码1
#include <DFRobot_BMP3XX.h>
/* If using Gravity products, choose these two interfaces and comment subsequent interfaces. */
// DFRobot_BMP388_I2C sensor;
// DFRobot_BMP390L_I2C sensor;
/**
* Select the chip version BMP388/BMP390L
* Select communication interface I2C, please comment out SPI interface.
* I2C communication address settings: eSDOGND: connect SDO pin to GND, I2C address is 0×76 now.
* eSDOVDD: Connect SDO pin to VDDIO (3v3), I2C address is 0×77 now
*/
// DFRobot_BMP388_I2C sensor(&Wire, sensor.eSDOVDD);
DFRobot_BMP390L_I2C sensor(&Wire, sensor.eSDOVDD);
/**
* Select chip version BMP388/BMP390L
* Select communication port SPI, please comment out I2C port
* Set up digital pin according to the on-board pin connected with SPI chip-select pin.
* Notice: csPin used here is D3 digital pin on ESP32, other non-conflicting pins can also be selected as external interrupt pins.
*/
// uint8_t csPin = D3;
// DFRobot_BMP388_SPI sensor(&SPI, csPin);
// DFRobot_BMP390L_SPI sensor(&SPI, csPin);
/* If you do not need to eliminate the absolute difference of measurement, please comment the following line */
#define CALIBRATE_ABSOLUTE_DIFFERENCE
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(115200);
int rslt;
while( ERR_OK != (rslt = sensor.begin()) ){
if(ERR_DATA_BUS == rslt){
Serial.println("Data bus error!!!");
}else if(ERR_IC_VERSION == rslt){
Serial.println("Chip versions do not match!!!");
}
delay(3000);
}
Serial.println("Begin ok!");
while( !sensor.setSamplingMode(sensor.eUltraPrecision) ){
Serial.println("Set samping mode fail, retrying....");
delay(3000);
}
delay(100);
#ifdef CALIBRATE_ABSOLUTE_DIFFERENCE
if( sensor.calibratedAbsoluteDifference(540.0) ){
Serial.println("Absolute difference base value set successfully!");
}
#endif
float sampingPeriodus = sensor.getSamplingPeriodUS();
Serial.print("samping period : ");
Serial.print(sampingPeriodus);
Serial.println(" us");
float sampingFrequencyHz = 1000000 / sampingPeriodus;
Serial.print("samping frequency : ");
Serial.print(sampingFrequencyHz);
Serial.println(" Hz");
Serial.println();
delay(1000);
}
void loop()
{
float temperature = sensor.readTempC();
Serial.print("temperature : ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" C");
float Pressure = sensor.readPressPa();
Serial.print("Pressure : ");
Serial.print(Pressure);
Serial.println(" Pa");
float altitude = sensor.readAltitudeM();
Serial.print("Altitude : ");
Serial.print(altitude);
Serial.println(" m");
Serial.println();
delay(1000);
}
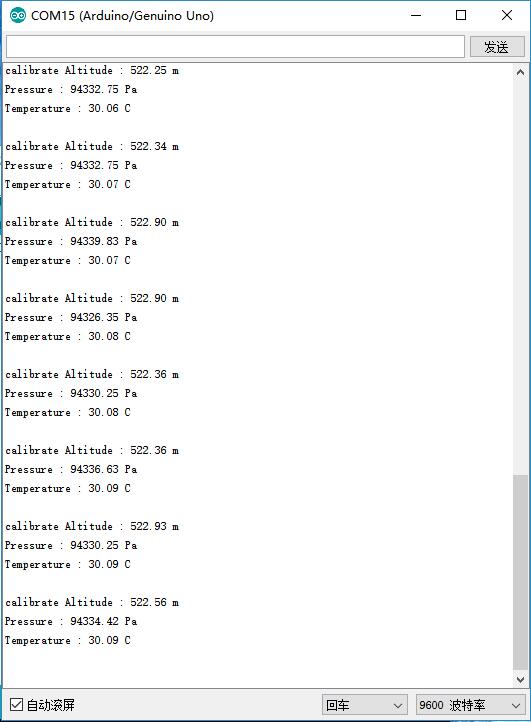
结果
- 在串口查看读取到的值
样例代码2
- 使用SPI通讯
/*!
* @file interruptDataDrdy.ino
* @brief Demonstrate ready data (temperature/pressure) interrupt
* @details When measured data, the sensor will generate a 2.5 ms pulse signal by INT in the non-interrupt
* [url=home.php?mod=space&uid=821650]@N[/url] register locked state.
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2010 DFRobot Co.Ltd (http://www.dfrobot.com)
* @license The MIT License (MIT)
* @author [qsjhyy](yihuan.huang@dfrobot.com)
* @version V1.0
* @date 2021-04-30
* @url https://github.com/DFRobot/DFRobot_BMP3XX
*/
#include <DFRobot_BMP3XX.h>
/**
* Select chip version BMP388/BMP390L
* Select I2C communication interface, please comment out SPI interface.
* I2C communication address settings: eSDOGND: connect SDO pin to GND, I2C address is 0×76 now.
* eSDOVDD: Connect SDO pin to VDDIO (3v3), I2C address is 0×77 now
* Notice: If using Gravity products, default I2C communication address is: 0×77(eSDOVDD)
*/
//DFRobot_BMP388_I2C sensor(&Wire, sensor.eSDOVDD);
//DFRobot_BMP390L_I2C sensor(&Wire, sensor.eSDOVDD);
/**
* Select the chip version BMP388/BMP390L
* Select I2C communication interface, please comment out SPI interface.
* Set up digital pin according to the on-board pin connected with SPI chip-select pin.
* Notice: csPin used here is D3 digital pin on ESP32, other non-conflicting pins can also be selected
* as external interrupt pins.
*/
uint8_t csPin = 4;
DFRobot_BMP388_SPI sensor(&SPI, csPin);
// DFRobot_BMP390L_SPI sensor(&SPI, csPin);
/* If you do not need to eliminate the absolute difference of measurement, please comment the following line */
#define CALIBRATE_ABSOLUTE_DIFFERENCE
/* Interrupt flag */
volatile uint8_t flag = 0;
/* External interrupt flag */
void interrupt()
{
if(flag ==0){
flag = 1;
}
}
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(115200);
int rslt;
while( ERR_OK != (rslt = sensor.begin()) ){
if(ERR_DATA_BUS == rslt){
Serial.println("Data bus error!!!");
}else if(ERR_IC_VERSION == rslt){
Serial.println("Chip versions do not match!!!");
}
delay(3000);
}
Serial.println("Begin ok!");
/**
* Interrupt configuration
* mode The interrupt mode needs to set. The following modes add up to mode:
* Interrupt pin output mode: eINTPinPP: Push pull, eINTPinOD: Open drain
* Interrupt pin active level: eINTPinActiveLevelLow: Active low, eINTPinActiveLevelHigh: Active high
* Register interrupt latch: eINTLatchDIS: Disable, eINTLatchEN: Enable
* FIFO water level reached interrupt: eIntFWtmDis: Disable, eIntFWtmEn: Enable
* FIFO full interrupt: eINTFFullDIS: Disable, eINTFFullEN: Enable
* Interrupt pin initial (invalid, non-interrupt) level: eINTInitialLevelLOW: Low, eINTInitialLevelHIGH: High
* Temperature/pressure data ready interrupt: eINTDataDrdyDIS: Disable, eINTDataDrdyEN: Enable
* Notice: In non-latching mode (eINTLatchDIS), interrupt signal is 2.5 ms pulse signal
* Note: When using eINTPinActiveLevelLow (Active low interrupt pin), you need to use eINTInitialLevelHIGH (Initial
* level of interrupt pin is high). Please use “FALLING” to trigger the following interrupt.
* When using eINTPinActiveLevelHigh (Active low interrupt pin), you need to use eINTInitialLevelLOW (Initial
* level of interrupt pin is high). Please use “RISING” to trigger the following interrupt.
*/
sensor.setINTMode(sensor.eINTPinPP |
sensor.eINTPinActiveLevelHigh |
sensor.eINTLatchDIS |
sensor.eIntFWtmDis |
sensor.eINTFFullDIS |
sensor.eINTInitialLevelLOW |
sensor.eINTDataDrdyEN);
delay(100);
#ifdef CALIBRATE_ABSOLUTE_DIFFERENCE
/**
* Calibrate the sensor according to the current altitude
* In this example, we use an altitude of 540 meters in Wenjiang District of Chengdu (China).
* Please change to the local altitude when using it.
* If this interface is not called, the measurement data will not eliminate the absolute difference
* Note: This interface is only valid for the first call
*/
if( sensor.calibratedAbsoluteDifference(540.0) ){
Serial.println("Absolute difference base value set successfully!");
}
#endif
#if defined(ESP32) || defined(ESP8266)
// D6 pin is used as interrupt pin by default, other non-conflicting pins can also be selected as external interrupt pins.
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(D6)/* Query the interrupt number of the D6 pin */,interrupt,CHANGE);
#elif defined(Arduino_SAM_ZERO)
// Pin 5 is used as interrupt pin by default, other non-conflicting pins can also be selected as external interrupt pins
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(5)/* Query the interrupt number of the 5 pin */,interrupt,CHANGE);
#else
/* The Correspondence Table of AVR Series Arduino Interrupt Pins And Terminal Numbers
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* | | DigitalPin | 2 | 3 | |
* | Uno, Nano, Mini, other 328-based |--------------------------------------------|
* | | Interrupt No | 0 | 1 | |
* |-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
* | | Pin | 2 | 3 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 |
* | Mega2560 |--------------------------------------------|
* | | Interrupt No | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
* |-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
* | | Pin | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 7 | |
* | Leonardo, other 32u4-based |--------------------------------------------|
* | | Interrupt No | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
* |--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* The Correspondence Table of micro:bit Interrupt Pins And Terminal Numbers
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* | micro:bit | DigitalPin |P0-P20 can be used as an external interrupt |
* | (When using as an external interrupt, |---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
* |no need to set it to input mode with pinMode)|Interrupt No|Interrupt number is a pin digital value, such as P0 interrupt number 0, P1 is 1 |
* |-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
*/
attachInterrupt(/*Interrupt No*/1,interrupt,CHANGE); // Open the external interrupt 0, connect INT1/2 to the digital pin of the main control:
// UNO(2), Mega2560(2), Leonardo(3), microbit(P0).
#endif
/* Get the sampling period of the current measurement mode, unit: us */
float sampingPeriodus = sensor.getSamplingPeriodUS();
Serial.print("samping period : ");
Serial.print(sampingPeriodus);
Serial.println(" us");
/* Get the sampling frequency of the current measurement mode, unit: Hz */
float sampingFrequencyHz = 1000000 / sampingPeriodus;
Serial.print("samping frequency : ");
Serial.print(sampingFrequencyHz);
Serial.println(" Hz");
Serial.println();
delay(1000);
}
void loop()
{
if(flag == 1){
flag = 0;
/* When data is ready and the interrupt is triggered, read altitude, unit: m */
float altitude = sensor.readAltitudeM();
Serial.print("Altitude : ");
Serial.print(altitude);
Serial.println(" m");
}
}
Mind+ 上传模式编程
- 下载及安装软件。下载地址:https://www.mindplus.cc 详细教程:Mind+基础wiki教程-软件下载安装
- 切换到“上传模式”。 详细教程:Mind+基础wiki教程-上传模式编程流程
- “扩展”中选择“主控板”中的“Arduino Uno”。 “扩展”“传感器”中搜索选择“BMP388模块”,详细教程:Mind+基础wiki教程-加载扩展库流程
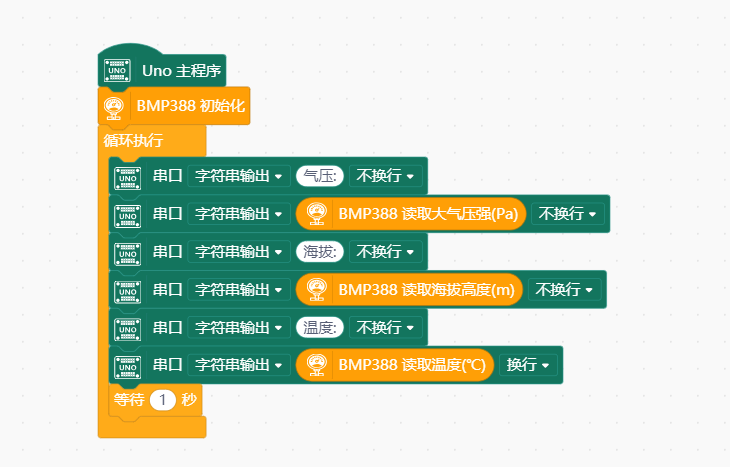
- 进行编程,程序如下图:
- 菜单“连接设备”,“上传到设备”
- 程序上传完毕后,打开串口即可看到数据输出。详细教程:Mind+基础wiki教程-串口打印
Mind+ Python模式编程(行空板)
Mind+Python模式为完整Python编程,因此需要能运行完整Python的主控板,此处以行空板为例说明
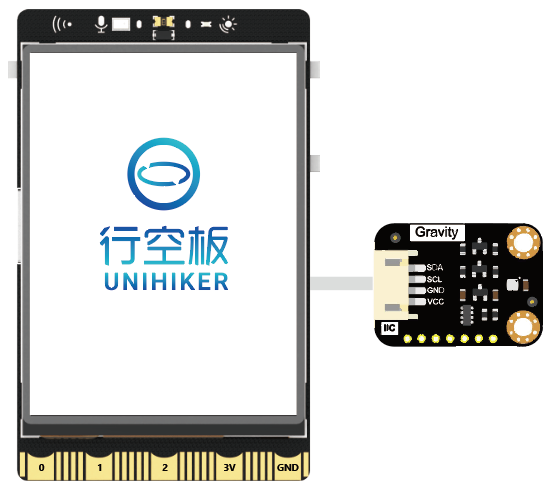
连接图
操作步骤
1、下载及安装官网最新软件。下载地址:https://www.mindplus.cc 详细教程:Mind+基础wiki教程-软件下载安装
2、切换到“Python模式”。“扩展”中选择“官方库”中的“行空板”和“pinpong库”中的”pinpong初始化“和“BMP388气压温度传感器。切换模式和加载库的详细操作链接
3、进行编程
4、连接行空板,程序点击运行后,可在终端查看数据。行空板官方文档-行空板快速上手教程 (unihiker.com)

代码编程
以pinpong库为例,行空板官方文档-行空板快速上手教程 (unihiker.com)
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# MindPlus
# Python
from pinpong.libs.dfrobot_bmp388 import BMP388
from pinpong.board import Board
import time
Board().begin()
bmp = BMP388()
while True:
print("大气压强:")
print(bmp.pressure_pa())
print("海拔高度:")
print(bmp.cal_altitude_m())
print("温度:")
print(bmp.temp_C())
time.sleep(1)
常见问题
1.此传感器如何和UNO SPI通信?
参考此贴:https://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/thread-316875-1-1.html
2.禁用温度采集后,高度(气压)采集数据会漂移(以一定速度变大或变小,明显超过正常范围且停不下来)?
温度本来就是为了校准气压的,测量气压的时候,不能禁用温度采集。
更多问题及有趣的应用,可以 访问论坛 进行查阅或发帖。
