简介
二氧化碳是一种无色无味的气体,它是大气重要组成成分之一。但CO2的过度排放、含量过高会产生温室效应等多种影响,还会危害人类和动植物的健康。
当环境中的二氧化碳浓度达到0.3%时人们会出现明显的头痛,达到4%-5%时会感到眩晕。室内环境尤其是在空调房间,环境相对密封,如果长时间不通风换气,二氧化碳浓度会逐渐升高,对人体健康不利,根据2003年实施的室内空气质量标准,日平均二氧化碳含量体积分数标准值不超过0.1%。而对于农作物,二氧化碳是光合作用的主要反应物,其浓度大小直接关系到农作物的光合效率,决定着农作物的生长发育,成熟期,抗逆性,质量,产量等。家庭中的空气净化设备,商场中的新风系统,大棚和畜牧场中的换气设备等,均是为了确保人类和动植物有优质的空气环境。而在这些设备中,也都少不了二氧化碳传感器的身影。
DFRobot为您带来的这款CO2传感器。采用工业级的MG-811 CO2探头,对CO2极为敏感,同时还能排除酒精和CO的干扰。该探头对环境温湿度的依赖小,性能稳定,快速恢复响应。模块自带信号放大电路,进一步提高灵敏度。另外,板载的升压电路使模块可以兼容3.3~5V DC的输入电压,保证了探头加热所需的6V DC供电,提高了模块适应性。它可以告诉你室内空气的质量,及时开窗降低CO2浓度。CO2浓度越高,输出的电压值就越小。通过我们的说明书和样例代码,用户可以轻松的读取CO2数值。用户还可以用板子上的电位器直接设置阈值,当CO2浓度高达一定程度时,探头旁边的3P-2.54排针会输出一个高电平信号(数字量)。
 注意 注意 |
|---|
| 本产品采用的MG-811探头属于电化学传感器,为得到更精确的测量值,请先对传感器进行标定操作。 |
| 本产品工作时需对探头加热,耗电较大,因此使用本产品时,Arduino主控板必须外接供电(7.5V-9V),否则会造成电压不稳,导致测量数据不准确。 |
产品参数
-
检测气体:二氧化碳
-
传感器探头工作电压:6v
-
模块工作电压:3.3~5V DC(电源电流大于500mA)
-
兼容蜂鸣器,通过调节板载金属电位器,可快速实现CO2超标蜂鸣器警报功能
-
输出信号:模拟量(0-5V)
-
沉金工艺,金色质感
-
尺寸:32*42mm
-
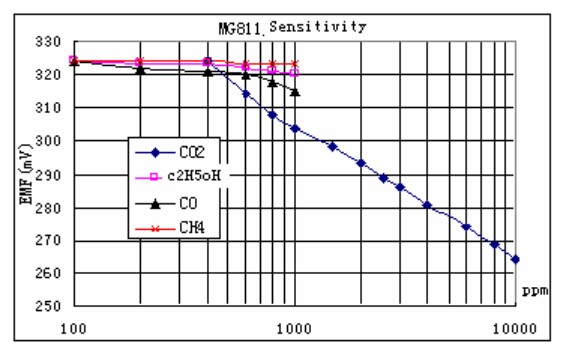
MG-811探头特性曲线表
Arduino使用教程
根据教程将传感器校准后,将程序下载到DFRuino UNO R3开发板,打开串口监视器查看二氧化碳浓度。
注意:
- 初次上电建议预热24~48小时。
- 电位器用来设置阀值,当设置的阀值小于测得的数值时,数字输出口便输出一个高电平。你可以在数字输出口接蜂鸣器模块或者LED模块用作报警显示。。
软硬件准备
- 硬件
- DFRuino UNO R3 x1
- SEN0159 CO2 二氧化碳传感器模块 x1
- 杜邦线 若干
- 软件
- Arduino IDE 点击下载Arduino IDE
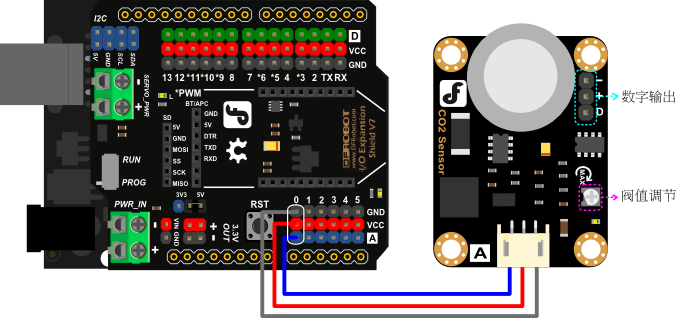
连线图
**注意:**本产品工作时需要对探头加热,耗电较大,因此使用本产品时,Arduino主控板必须外接供电(7.5V-9V),否则会造成电压不稳,导致测量数据不准确。
标定操作
本模块采用的MG-811探头属于电化学传感器,为得到更精确的测量值,请先对传感器进行标定操作。
①给模块提供稳定的电源,并将模块放置在空气清新的地方,连续加热48小时。
②使用万用表或Arduino模拟量读取的方式,测量模块的输出电压(GND和A两端),将输出电压值(单位:V)除以8.5,得到的数值填入代码中的宏定义部分,如下列代码所示:
#define ZERO_POINT_VOLTAGE (括号中改成:电压值(V)/8.5)
例如,用万用表测量CO2模块输出的电压为2.4V,那么2.4/8.5=0.282, 则修改如下:
#define ZERO_POINT_VOLTAGE (0.282)
代码修改完,重新上传至DFRuino UNO R3主控板。至此,标定就完成了。之后即可用于实际的测量。
样例代码
- 将模块与Arduino按照上方的连线图相连,当配合Gravity I/O扩展板使用,可以更方便、更快速的完成项目原型搭建。
- 打开Arduino IDE,将下面的代码上传到DFRuino UNO R3开发板。
- 打开Arduino IDE的串口监控视器,把波特率调至9600,观察串口打印结果。
/*******************Demo for MG-811 Gas Sensor Module V1.1*****************************
Author: Tiequan Shao: tiequan.shao@sandboxelectronics.com
Peng Wei: peng.wei@sandboxelectronics.com
Lisence: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0)
Note: This piece of source code is supposed to be used as a demostration ONLY. More
sophisticated calibration is required for industrial field application.
Sandbox Electronics 2012-05-31
************************************************************************************/
/************************Hardware Related Macros************************************/
#define MG_PIN (A0) //define which analog input channel you are going to use
#define BOOL_PIN (2)
#define DC_GAIN (8.5) //define the DC gain of amplifier
/***********************Software Related Macros************************************/
#define READ_SAMPLE_INTERVAL (50) //define how many samples you are going to take in normal operation
#define READ_SAMPLE_TIMES (5) //define the time interval(in milisecond) between each samples in
//normal operation
/**********************Application Related Macros**********************************/
//These two values differ from sensor to sensor. user should derermine this value.
#define ZERO_POINT_VOLTAGE (0.220) //define the output of the sensor in volts when the concentration of CO2 is 400PPM
#define REACTION_VOLTGAE (0.030) //define the voltage drop of the sensor when move the sensor from air into 1000ppm CO2
/*****************************Globals***********************************************/
float CO2Curve[3] = {2.602,ZERO_POINT_VOLTAGE,(REACTION_VOLTGAE/(2.602-3))};
//two points are taken from the curve.
//with these two points, a line is formed which is
//"approximately equivalent" to the original curve.
//data format:{ x, y, slope}; point1: (lg400, 0.324), point2: (lg4000, 0.280)
//slope = ( reaction voltage ) / (log400 –log1000)
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //UART setup, baudrate = 9600bps
pinMode(BOOL_PIN, INPUT); //set pin to input
digitalWrite(BOOL_PIN, HIGH); //turn on pullup resistors
Serial.print("MG-811 Demostration\n");
}
void loop()
{
int percentage;
float volts;
volts = MGRead(MG_PIN);
Serial.print( "SEN0159:" );
Serial.print(volts);
Serial.print( "V " );
percentage = MGGetPercentage(volts,CO2Curve);
Serial.print("CO2:");
if (percentage == -1) {
Serial.print( "<400" );
} else {
Serial.print(percentage);
}
Serial.print( "ppm" );
Serial.print("\n");
if (digitalRead(BOOL_PIN) ){
Serial.print( "=====BOOL is HIGH======" );
} else {
Serial.print( "=====BOOL is LOW======" );
}
Serial.print("\n");
delay(500);
}
/***************************** MGRead *********************************************
Input: mg_pin - analog channel
Output: output of SEN-000007
Remarks: This function reads the output of SEN-000007
************************************************************************************/
float MGRead(int mg_pin)
{
int i;
float v=0;
for (i=0;i<READ_SAMPLE_TIMES;i++) {
v += analogRead(mg_pin);
delay(READ_SAMPLE_INTERVAL);
}
v = (v/READ_SAMPLE_TIMES) *5/1024 ;
return v;
}
/***************************** MQGetPercentage **********************************
Input: volts - SEN-000007 output measured in volts
pcurve - pointer to the curve of the target gas
Output: ppm of the target gas
Remarks: By using the slope and a point of the line. The x(logarithmic value of ppm)
of the line could be derived if y(MG-811 output) is provided. As it is a
logarithmic coordinate, power of 10 is used to convert the result to non-logarithmic
value.
************************************************************************************/
int MGGetPercentage(float volts, float *pcurve)
{
if ((volts/DC_GAIN )>=ZERO_POINT_VOLTAGE) {
return -1;
} else {
return pow(10, ((volts/DC_GAIN)-pcurve[1])/pcurve[2]+pcurve[0]);
}
}
结果
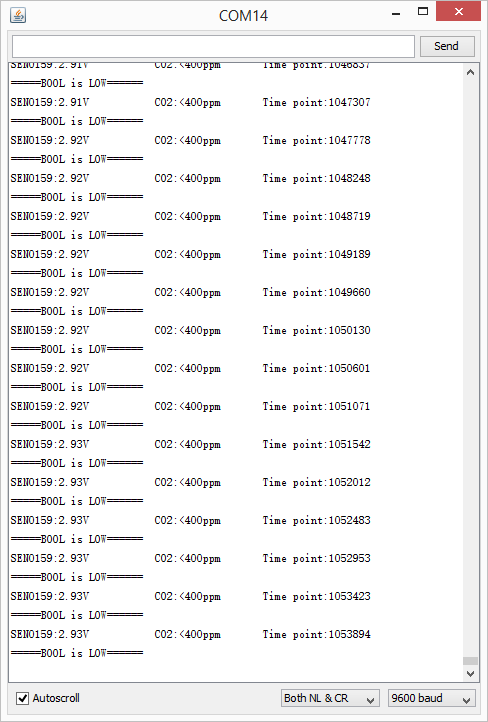
打开串口监视器,大约五分钟后,你会得到你周围二氧化碳浓度的数据。
常见问题
还没有客户对此产品有任何问题,欢迎通过qq或者论坛联系我们!
更多问题及有趣的应用,可以 访问论坛 进行查阅或发帖。
