简介
科技作为一种新美学,一直以来都难以被传统时尚界接受。谈到科技,总给人留下一种“怪咖”、“宅”的负面印象。此款产品将作为科技时尚的翻身之作,给你带来真正的科技美学。
Kitty’s Flower是一款蓝牙可穿戴控制器,由设计师Kitty Yeung和DFRobot联合打造,专为可穿戴应用场景设计,集成充电电源管理系统、RGB LED灯、加速度传感器、震动、触摸等硬件外设,支持Arduino和Scratch编程,可以作为可穿戴产品、交互艺术装置、新时装、新饰品上的核心智能控制单元。
技术规格
- 微控制器:ATmega328
- BLE芯片类型:TI CC2540
- 支持蓝牙HID
- 支持通过AT指令调试蓝牙模组
- 通过串口的透明通信
- USB升级BLE固件
- 供电接口:USB/3.7V锂电池
- 外部供电范围:7-12V
- Bootloader:Arduino UNO
- 尺寸:70mm*70mm
- 重量: 30g
引脚说明
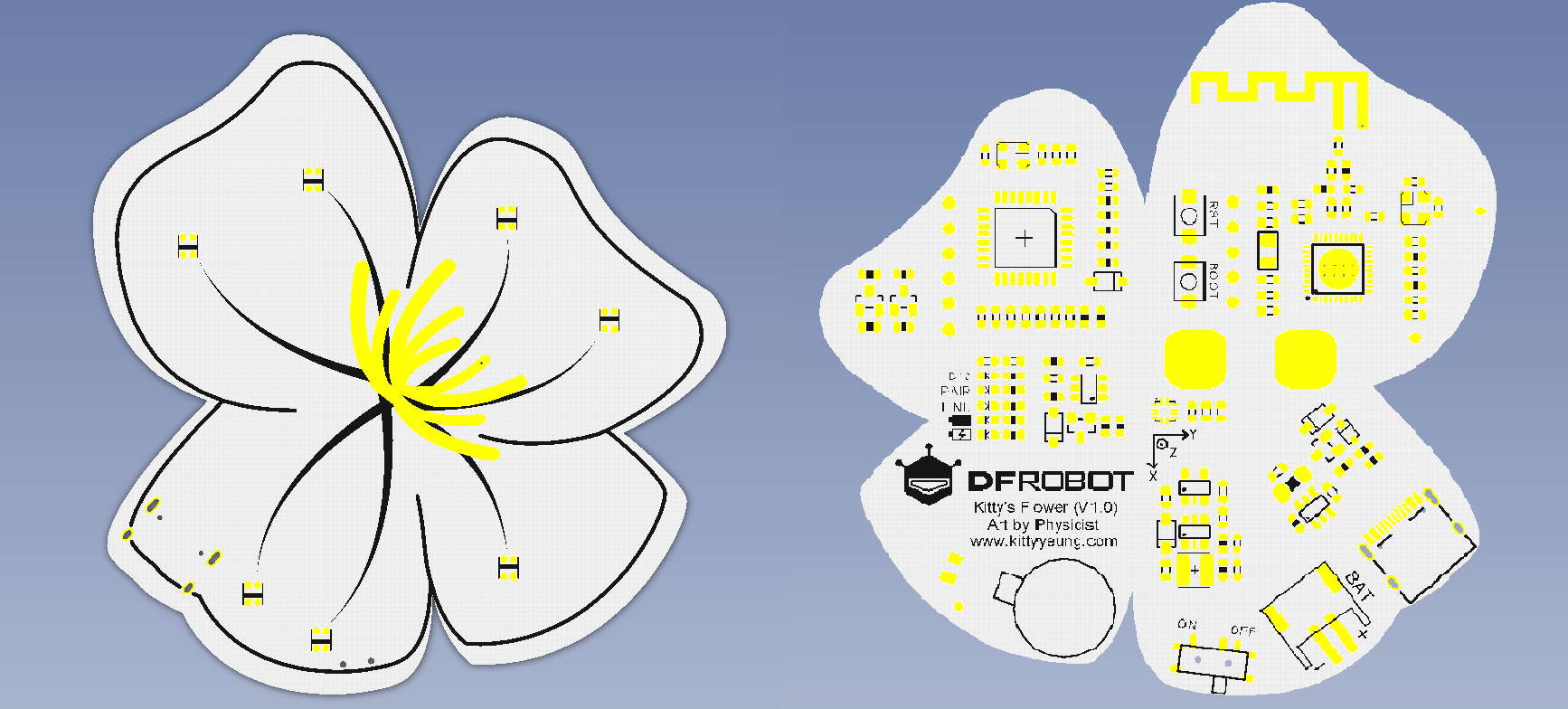
| 标号 | 名称 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 震动马达 | D5 |
| 2 | 触摸 | D6 |
| 3 | RGB LED | D9 |
| 4 | LIS2DH 三轴加速度计 | I2C |
使用教程
Kitty Flower集成多种功能,我们会在下方一一展示,但是实际使用中,请将Kitty Flowers分别烧录: KittyMother和KittyChild两个Demo即可完成配对和连接。两个Demo会自动设置主板的主/从机状态,然后读取蓝牙RSSI场强数值,从而判断相互间的距离。点击下载Kitty's Flower Demo分别烧录代码。以下是各功能的使用方法:
准备
- 硬件
- 1 x Kitty's Flower
- 软件
- Arduino IDE 点击下载Arduino IDE
震动马达样例代码
#define VMPIN 5 //Vibration motor pin
void setup() {
// initialize digital pin LED_BUILTIN as an output.
pinMode(VMPIN, OUTPUT);
}
// the loop function runs over and over again forever
void loop() {
digitalWrite(VMPIN, HIGH); // turn the Motor on (HIGH is the voltage level)
delay(1000); // wait for a second
digitalWrite(VMPIN, LOW); // turn the Motor off by making the voltage LOW
delay(1000); // wait for a second
}
震动电机会反复一震一停
触摸样例代码
#define TOUCHPIN 6
void setup() {
// initialize serial communication at 9600 bits per second:
Serial.begin(115200);
// make the pushbutton's pin an input:
pinMode(TOUCHPIN, INPUT);
}
// the loop routine runs over and over again forever:
void loop() {
// read the input pin:
int touchState = digitalRead(TOUCHPIN);
// print out the state of the button:
Serial.println(touchState);
delay(10); // delay in between reads for stability
}
打开串口,触摸花蕊,串口输出高电平;反之输出低电平
RGB LED样例代码
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 9 //The signal pin connected with Arduino
#define LED_COUNT 60 // the amount of the leds of your strip
// Create an instance of the Adafruit_NeoPixel class called "leds".
// That'll be what we refer to from here on...
Adafruit_NeoPixel leds = Adafruit_NeoPixel(LED_COUNT, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup()
{
leds.begin(); // Call this to start up the LED strip.
clearLEDs(); // This function, defined below, turns all LEDs off...
leds.show(); // ...but the LEDs don't actually update until you call this.
}
void loop()
{
for (int i=0; i<LED_COUNT; i++)
{
rainbow(i);
delay(10); // Delay between rainbow slides
}
}
// Sets all LEDs to off, but DOES NOT update the display;
// call leds.show() to actually turn them off after this.
void clearLEDs()
{
for (int i=0; i<LED_COUNT; i++)
{
leds.setPixelColor(i, 0);
}
}
// Prints a rainbow on the ENTIRE LED strip.
// The rainbow begins at a specified position.
// ROY G BIV!
void rainbow(byte startPosition)
{
// Need to scale our rainbow. We want a variety of colors, even if there
// are just 10 or so pixels.
int rainbowScale = 192 / LED_COUNT;
// Next we setup each pixel with the right color
for (int i=0; i<LED_COUNT; i++)
{
// There are 192 total colors we can get out of the rainbowOrder function.
// It'll return a color between red->orange->green->...->violet for 0-191.
leds.setPixelColor(i, rainbowOrder((rainbowScale * (i + startPosition)) % 192));
}
// Finally, actually turn the LEDs on:
leds.show();
}
// Input a value 0 to 191 to get a color value.
// The colors are a transition red->yellow->green->aqua->blue->fuchsia->red...
// Adapted from Wheel function in the Adafruit_NeoPixel library example sketch
uint32_t rainbowOrder(byte position)
{
// 6 total zones of color change:
if (position < 31) // Red -> Yellow (Red = FF, blue = 0, green goes 00-FF)
{
return leds.Color(0xFF, position * 8, 0);
}
else if (position < 63) // Yellow -> Green (Green = FF, blue = 0, red goes FF->00)
{
position -= 31;
return leds.Color(0xFF - position * 8, 0xFF, 0);
}
else if (position < 95) // Green->Aqua (Green = FF, red = 0, blue goes 00->FF)
{
position -= 63;
return leds.Color(0, 0xFF, position * 8);
}
else if (position < 127) // Aqua->Blue (Blue = FF, red = 0, green goes FF->00)
{
position -= 95;
return leds.Color(0, 0xFF - position * 8, 0xFF);
}
else if (position < 159) // Blue->Fuchsia (Blue = FF, green = 0, red goes 00->FF)
{
position -= 127;
return leds.Color(position * 8, 0, 0xFF);
}
else //160 <position< 191 Fuchsia->Red (Red = FF, green = 0, blue goes FF->00)
{
position -= 159;
return leds.Color(0xFF, 0x00, 0xFF - position * 8);
}
}
加速度代码
#include <Wire.h>
#include <DFRobot_LIS2DH12.h>
DFRobot_LIS2DH12 LIS; //Accelerometer
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial);
delay(100);
// Set measurement range
// Ga: LIS2DH12_RANGE_2GA
// Ga: LIS2DH12_RANGE_4GA
// Ga: LIS2DH12_RANGE_8GA
// Ga: LIS2DH12_RANGE_16GA
while (LIS.init(LIS2DH12_RANGE_16GA) == -1) { //Equipment connection exception or I2C address error
Serial.println("No I2C devices found");
delay(1000);
}
}
void loop() {
acceleration();
}
/*!
@brief Print the position result.
*/
void acceleration(void)
{
int16_t x, y, z;
delay(100);
LIS.readXYZ(x, y, z);
LIS.mgScale(x, y, z);
Serial.print("Acceleration x: "); //print acceleration
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(" mg \ty: ");
Serial.print(y);
Serial.print(" mg \tz: ");
Serial.print(z);
Serial.println(" mg");
}
结果
常见问题
还没有客户对此产品有任何问题,欢迎通过qq或者论坛联系我们!
更多问题及有趣的应用,可以 访问论坛 进行查阅或发帖。


