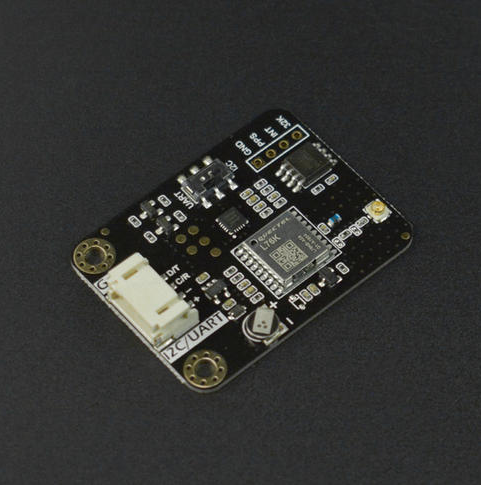
简介
该产品是一款集成了GNSS和RTC芯片的模块。可接收北斗、GPS等多种卫星信号,获取准确的时间信息,并为RTC校时,以确保时间的高精度和稳定性。它为用户提供了一种简单、便捷的方式来校准和维护设备的时间,适用于各种需要精确时间同步的应用场景。
在无法获取GNSS信号的情况下,可以使用板载的RTC芯片获取时间。
当在户外需要低功耗的的场景中,也可以通过API切断GNSS的供电来大幅降低功耗。
产品参数
-
工作电压: 3.3V~5V DC
-
输出信号:I2C/UART
-
定位精度:2.0m CEP
-
首次定位时间:冷启动30S 热启动2S
-
功耗:46mA(GNSS芯片开启), <1mA (GNSS芯片关闭)。以上均为5V状况测试。
-
天线接口: IPEX一代
-
产品尺寸:32mm * 42mm
引脚说明
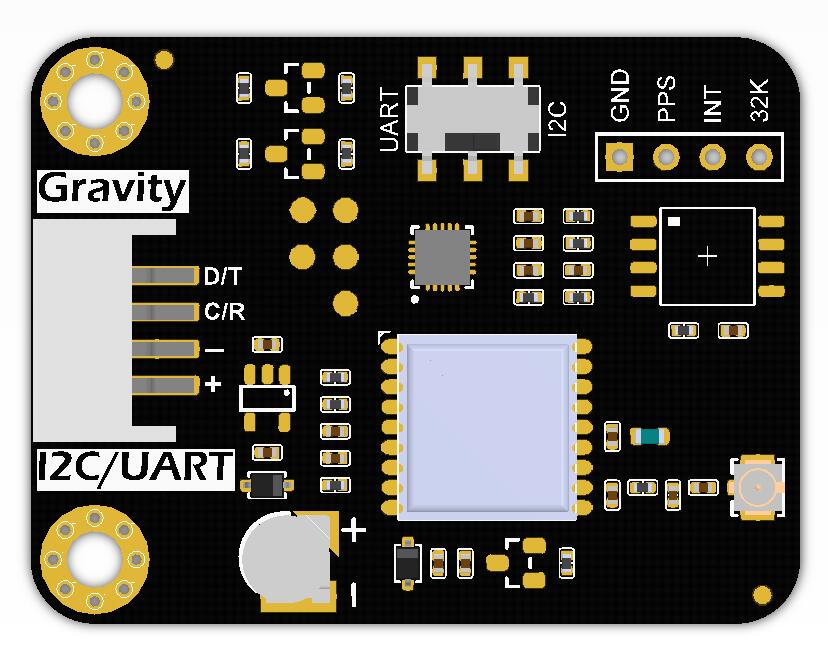
| 标号 | 名称 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | D/T | I2C数据线SDA UART数据传输-TX |
| 2 | C/R | I2C时钟线SCL UART数据接收-RX |
| 3 | - | GND电源负极 |
| 4 | + | 电源正极 |
| 5 | PPS | GNSS芯片每秒脉冲输出 |
| 6 | INT | 低电平有效中断或者1Hz方波输出 |
| 7 | 32K | 32.768KHz脉冲输出 |
Arduino使用教程
一、软硬件准备
-
硬件
-
软件
- Arduino IDE 点击下载Arduino IDE
- 下载并安装DFRobot_GNSS and RTC库
-
接线图

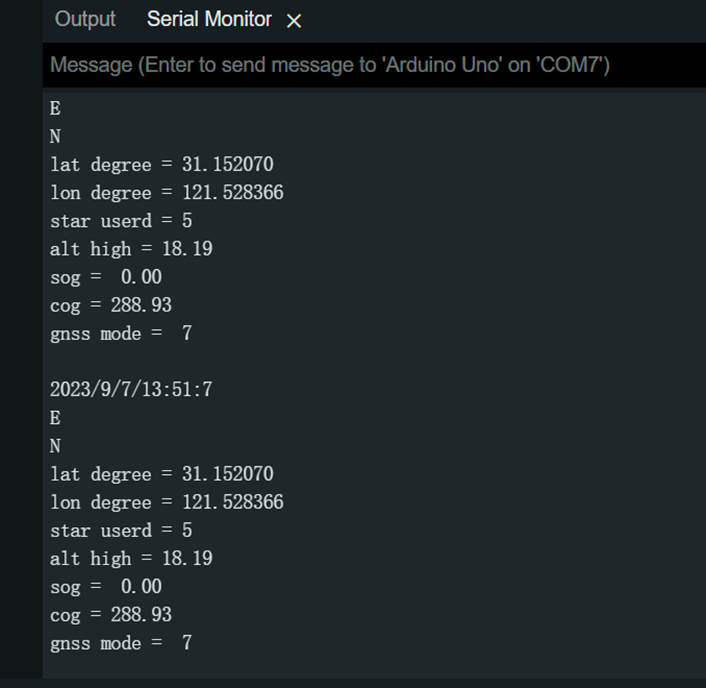
样例代码 1 - 获取GNSS定位
调用所有GNSS相关API,获得经纬度,卫星数量,卫星数量等参数。
示例代码为I2C通讯。
/*!
* @file getGNSS.ino
* @brief Get gnss simple data
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2010 DFRobot Co.Ltd (http://www.dfrobot.com)
* @license The MIT License (MIT)
* @author [qsjhyy](yihuan.huang@dfrobot.com)
* @version V1.0
* @date 2022-08-30
* @url https://github.com/DFRobot/DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC
*/
#include "DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC.h"
#define I2C_COMMUNICATION //use I2C for communication, but use the serial port for communication if the line of codes were masked
#ifdef I2C_COMMUNICATION
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC_I2C gnss(&Wire, MODULE_I2C_ADDRESS);
#else
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* board | MCU | Leonardo/Mega2560/M0 | UNO | ESP8266 | ESP32 | microbit | m0 |
* VCC | 3.3V/5V | VCC | VCC | VCC | VCC | X | vcc |
* GND | GND | GND | GND | GND | GND | X | gnd |
* RX | TX | Serial1 TX1 | 5 | 5/D6 | D2 | X | tx1 |
* TX | RX | Serial1 RX1 | 4 | 4/D7 | D3 | X | rx1 |
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Baud rate cannot be changed */
#if defined(ARDUINO_AVR_UNO) || defined(ESP8266)
SoftwareSerial mySerial(4, 5);
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC_UART gnss(&mySerial, UART_BAUDRATE);
#elif defined(ESP32)
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC_UART gnss(&Serial1, UART_BAUDRATE,/*rx*/D2,/*tx*/D3);
#else
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC_UART gnss(&Serial1, UART_BAUDRATE);
#endif
#endif
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!gnss.begin()) {
Serial.println("NO Deivces !");
delay(1000);
}
gnss.enablePower(); // Enable gnss power
/** Set GNSS to be used
* eGPS use gps
* eBeiDou use beidou
* eGPS_BeiDou use gps + beidou
* eGLONASS use glonass
* eGPS_GLONASS use gps + glonass
* eBeiDou_GLONASS use beidou +glonass
* eGPS_BeiDou_GLONASS use gps + beidou + glonass
*/
gnss.setGnss(gnss.eGPS_BeiDou_GLONASS);
// gnss.disablePower(); // Disable GNSS, the data will not be refreshed after disabling
}
void loop()
{
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC::sTim_t utc = gnss.getUTC();
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC::sTim_t date = gnss.getDate();
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC::sLonLat_t lat = gnss.getLat();
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC::sLonLat_t lon = gnss.getLon();
double high = gnss.getAlt();
uint8_t starUserd = gnss.getNumSatUsed();
double sog = gnss.getSog();
double cog = gnss.getCog();
Serial.println("");
Serial.print(date.year);
Serial.print("/");
Serial.print(date.month);
Serial.print("/");
Serial.print(date.date);
Serial.print("/");
Serial.print(utc.hour);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(utc.minute);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(utc.second);
Serial.println();
Serial.println((char)lat.latDirection);
Serial.println((char)lon.lonDirection);
// Serial.print("lat DDMM.MMMMM = ");
// Serial.println(lat.latitude, 5);
// Serial.print("lon DDDMM.MMMMM = ");
// Serial.println(lon.lonitude, 5);
Serial.print("lat degree = ");
Serial.println(lat.latitudeDegree, 6);
Serial.print("lon degree = ");
Serial.println(lon.lonitudeDegree, 6);
Serial.print("star userd = ");
Serial.println(starUserd);
Serial.print("alt high = ");
Serial.println(high);
Serial.print("sog = ");
Serial.println(sog);
Serial.print("cog = ");
Serial.println(cog);
Serial.print("gnss mode = ");
Serial.println(gnss.getGnssMode());
delay(1000);
}
结果
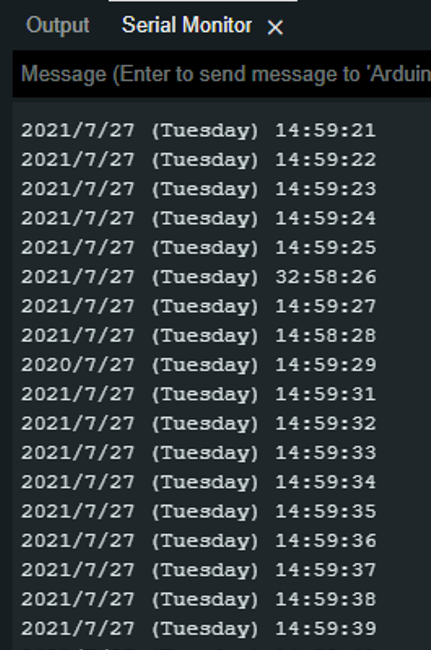
样例代码 2 - 获取RTC时间
获取授时模块板载RTC芯片的时间。
此示例代码为I2C通讯
/*!
* @file getTime.ino
* @brief Run this routine, set internal clock first, and then circularly get clock, temperature and voltage data
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2010 DFRobot Co.Ltd (http://www.dfrobot.com)
* @license The MIT License (MIT)
* @author [qsjhyy](yihuan.huang@dfrobot.com)
* @version V1.0
* @date 2022-08-30
* @url https://github.com/DFRobot/DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC
*/
#include "DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC.h"
#define I2C_COMMUNICATION //use I2C for communication, but use the serial port for communication if the line of codes were masked
#ifdef I2C_COMMUNICATION
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC_I2C rtc(&Wire, MODULE_I2C_ADDRESS);
#else
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* board | MCU | Leonardo/Mega2560/M0 | UNO | ESP8266 | ESP32 | microbit | m0 |
* VCC | 3.3V/5V | VCC | VCC | VCC | VCC | X | vcc |
* GND | GND | GND | GND | GND | GND | X | gnd |
* RX | TX | Serial1 TX1 | 5 | 5/D6 | D2 | X | tx1 |
* TX | RX | Serial1 RX1 | 4 | 4/D7 | D3 | X | rx1 |
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Baud rate cannot be changed */
#if defined(ARDUINO_AVR_UNO) || defined(ESP8266)
SoftwareSerial mySerial(4, 5);
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC_UART rtc(&mySerial, UART_BAUDRATE);
#elif defined(ESP32)
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC_UART rtc(&Serial1, UART_BAUDRATE,/*rx*/D2,/*tx*/D3);
#else
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC_UART rtc(&Serial1, UART_BAUDRATE);
#endif
#endif
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
/*Wait for the chip to be initialized completely, and then exit*/
while(!rtc.begin()){
Serial.println("Failed to init chip, please check if the chip connection is fine. ");
delay(1000);
}
rtc.setHourSystem(rtc.e24hours);//Set display format
rtc.setTime(2021,7,27,14,59,0);//Initialize time
// //Get internal temperature
// Serial.print(rtc.getTemperatureC());
// Serial.println(" C");
// //Get battery voltage
// Serial.print(rtc.getVoltage());
// Serial.println(" V");
}
void loop()
{
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC::sTimeData_t sTime;
sTime = rtc.getRTCTime();
Serial.print(sTime.year, DEC);//year
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(sTime.month, DEC);//month
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(sTime.day, DEC);//day
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(sTime.week);//week
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(sTime.hour, DEC);//hour
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(sTime.minute, DEC);//minute
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(sTime.second, DEC);//second
Serial.println(' ');
/*Enable 12-hour time format*/
// Serial.print(rtc.getAMorPM());
// Serial.println();
delay(1000);
}
结果
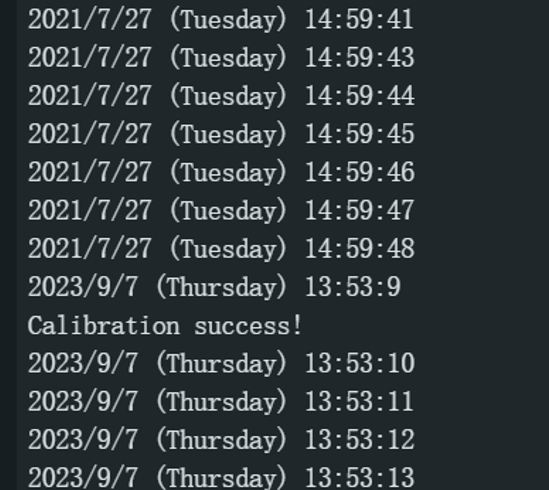
样例代码 3 - GNSS校准RTC时间
通过GNSS时间来校准RTC芯片。校时过程需要2~3秒,这段时间内无法正常获取时间。
校时完成后串行监视器打印"Calibration success"。
此示例代码为I2C通讯
/*!
* @file gnssCalibRTC.ino
* @brief Run this routine, calibration internal clock first, and then circularly get clock
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2010 DFRobot Co.Ltd (http://www.dfrobot.com)
* @license The MIT License (MIT)
* @author [qsjhyy](yihuan.huang@dfrobot.com)
* @version V1.0
* @date 2022-08-30
* @url https://github.com/DFRobot/DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC
*/
#include "DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC.h"
#define I2C_COMMUNICATION //use I2C for communication, but use the serial port for communication if the line of codes were masked
#ifdef I2C_COMMUNICATION
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC_I2C rtc(&Wire, MODULE_I2C_ADDRESS);
#else
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* board | MCU | Leonardo/Mega2560/M0 | UNO | ESP8266 | ESP32 | microbit | m0 |
* VCC | 3.3V/5V | VCC | VCC | VCC | VCC | X | vcc |
* GND | GND | GND | GND | GND | GND | X | gnd |
* RX | TX | Serial1 TX1 | 5 | 5/D6 | D2 | X | tx1 |
* TX | RX | Serial1 RX1 | 4 | 4/D7 | D3 | X | rx1 |
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Baud rate cannot be changed */
#if defined(ARDUINO_AVR_UNO) || defined(ESP8266)
SoftwareSerial mySerial(4, 5);
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC_UART rtc(&mySerial, UART_BAUDRATE);
#elif defined(ESP32)
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC_UART rtc(&Serial1, UART_BAUDRATE,/*rx*/D2,/*tx*/D3);
#else
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC_UART rtc(&Serial1, UART_BAUDRATE);
#endif
#endif
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
/*Wait for the chip to be initialized completely, and then exit*/
while (!rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to init chip, please check if the chip connection is fine. ");
delay(1000);
}
rtc.setHourSystem(rtc.e24hours);//Set display format
/**
* @brief Calibrate RTC immediately with GNSS
* @note This is a single calibration;
* @n If the GNSS module signal is weak, time calibration may encounter issues.
* @return None
*/
// rtc.calibRTC();
/**
* @brief The loop automatically performs GNSS timing based on the set interval
* @param hour Automatic calibration of the time interval. range: 0~255, unit: hour.
* @note When set to zero, automatic time calibration is disabled.
* @n Enabling it will trigger an immediate calibration.
* @n If the GNSS module signal is weak, time calibration may encounter issues.
* @return None
*/
rtc.calibRTC(1);
}
uint8_t underCalibCount = 0;
void loop()
{
/**
* @brief Current clock calibration status
* @param mode By default, it is set to true, indicating access to the calibration status only.
* @n If continuous calibration for one minute does not return a successful calibration,
* @n you can pass in false to manually terminate this calibration session.
* @return uint8_t type, indicates current clock calibration status
* @retval 0 Not calibrated
* @retval 1 Calibration complete
* @retval 2 Under calibration
* @note Note: To avoid affecting subsequent calibration status,
* @n "Calibration completed Status (1)" is automatically zeroed after a successful read
*/
uint8_t status = rtc.calibStatus();
if (DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC::eCalibComplete == status) {
underCalibCount = 0;
Serial.println("Calibration success!");
} else if (DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC::eUnderCalib == status) {
underCalibCount += 1;
if (60 <= underCalibCount) { // If the calibration fails for a long time, manually terminate the calibration
rtc.calibStatus(false);
underCalibCount = 0;
Serial.println("Calibration failed!");
Serial.println("It may be due to weak satellite signals.");
Serial.println("Please proceed to an open outdoor area for time synchronization.");
}
}
DFRobot_GNSSAndRTC::sTimeData_t sTime;
sTime = rtc.getRTCTime();
Serial.print(sTime.year, DEC);//year
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(sTime.month, DEC);//month
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(sTime.day, DEC);//day
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(sTime.week);//week
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(sTime.hour, DEC);//hour
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(sTime.minute, DEC);//minute
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(sTime.second, DEC);//second
Serial.println(' ');
/*Enable 12-hour time format*/
// Serial.print(rtc.getAMorPM());
// Serial.println();
// In addition to data acquisition and other time consuming, the delay of 900ms makes each loop closer to 1 second
delay(900);
}
结果
更多API接口函数列表
/**
* @fn calibRTC(void)
* @brief 立即使用GNSS来校准RTC时钟
* @note This is a single calibration;
* @n If the GNSS module signal is weak, time calibration may encounter issues.
* @return None
*/
void calibRTC(void);
/**
* @fn calibRTC(uint8_t hour)
* @brief 根据设定的时间间隔自动执行 GNSS 校准 RTC
* @param hour Automatic calibration of the time interval. range: 0~255, unit: hour.
* @note When set to zero, automatic time calibration is disabled.
* @n Enabling it will trigger an immediate calibration.
* @n If the GNSS module signal is weak, time calibration may encounter issues.
* @return None
*/
void calibRTC(uint8_t hour);
/**
* @fn calibStatus
* @brief 获取校准状态
* @param mode By default, it is set to true, indicating access to the calibration status only.
* @n If continuous calibration for one minute does not return a successful calibration,
* @n you can pass in false to manually terminate this calibration session.
* @return uint8_t type, indicates current clock calibration status
* @retval 0 Not calibrated
* @retval 1 Calibration complete
* @retval 2 Under calibration
* @note Note: To avoid affecting subsequent calibration status,
* @n "Calibration completed Status (1)" is automatically zeroed after a successful read
*/
uint8_t calibStatus(bool mode = true);
/**
* @fn setAlarm
* @brief 设置报警时间
* @param year 2000~2099
* @param month 1~12
* @param day 1~31
* @return None
*/
void setAlarm(uint16_t year, uint8_t month, uint8_t day);
/**
* @brief 清除报警
*/
void clearAlarm(void);
/**
* @fn enable32k
* @brief 使能32kHz方波输出
* @return None
*/
void enable32k();
/**
* @fn disable32k
* @brief 失能32kHz方波输出
* @return None
*/
void disable32k();
/**
* @fn countDown
* @brief 倒计时
* @param second countdown time 0-0xffffff
*/
void countDown(uint32_t second);
/**
* @fn getUTC
* @brief 获取UTC时间
* @return sTim_t type, represents the returned hour, minute and second
* @retval sTim_t.hour hour
* @retval sTim_t.minute minute
* @retval sTim_t.second second
*/
sTim_t getUTC(void);
/**
* @fn enablePower
* @brief 使能GNSS电源
* @return null
*/
void enablePower(void);
/**
* @fn disablePower
* @brief 失能GNSS电源
* @return null
*/
void disablePower(void);
Mind+ 上传模式编程
1.下载及安装软件。下载地址:https://www.mindplus.cc
2.切换到“上传模式”。
3.“扩展”中选择“主控板”中的“Arduino UNO”。用户库加载:https://gitee.com/chenqi1233/ext-gravity-gnss-pt
4.进行编程,程序如下图
5.菜单“链接设备”,“上传到设备”
6.程序上传完毕后,打开串口即可看到数据输出。

常见问题
-
Q1校准RTC芯片过,但是断电后读取RTC,发现时间不正确
A1.RTC芯片需要消耗电量来维持时间,我们板载设计了超级电容在整个模块断电时为其提供电量。
经过测试,超级电容中的电量会在模块断电后10~20分钟左右耗尽。
所以在断电后,RTC时间仅能维持10~20分钟。
我们建议您在重新为其上电的时候用GNSS芯片校准一次RTC时间。 -
Q2 校准时间后,发现小时读数不正确
A2.卫星校准时间是使用UTC时间的,国内的北京时间需要UTC+8小时。

