概述
这是一款音频信号分析模块,而且更新到了V2版这款模块的设计基于MSGEQ7图形均衡滤波器。音频信号通过该模块会被过滤成7个波段。并且能够输出每一个频段的幅值。这七个频段分别是:63Hz,160Hz,400Hz,1KHz,2.5kHz,6.25kHz和16kHz。
这个模块可以用于创建一个音频分析器,追踪音乐的频率信息让你的控制器(Arduino)和音乐带起互动。
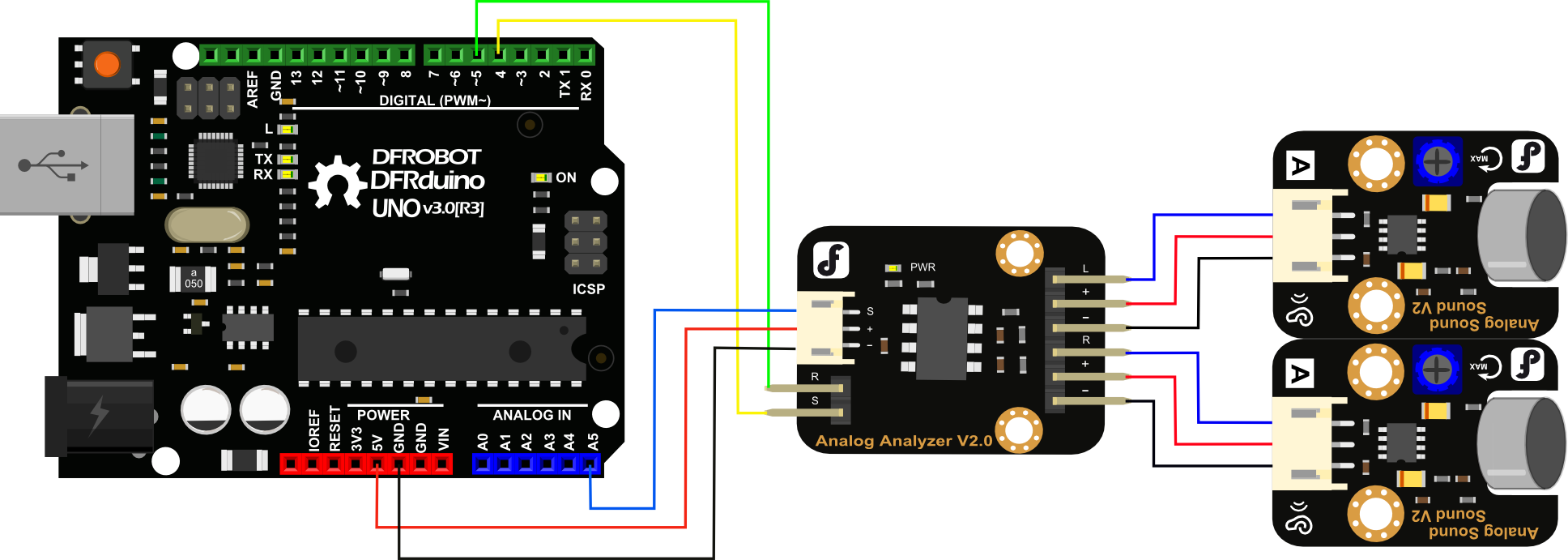
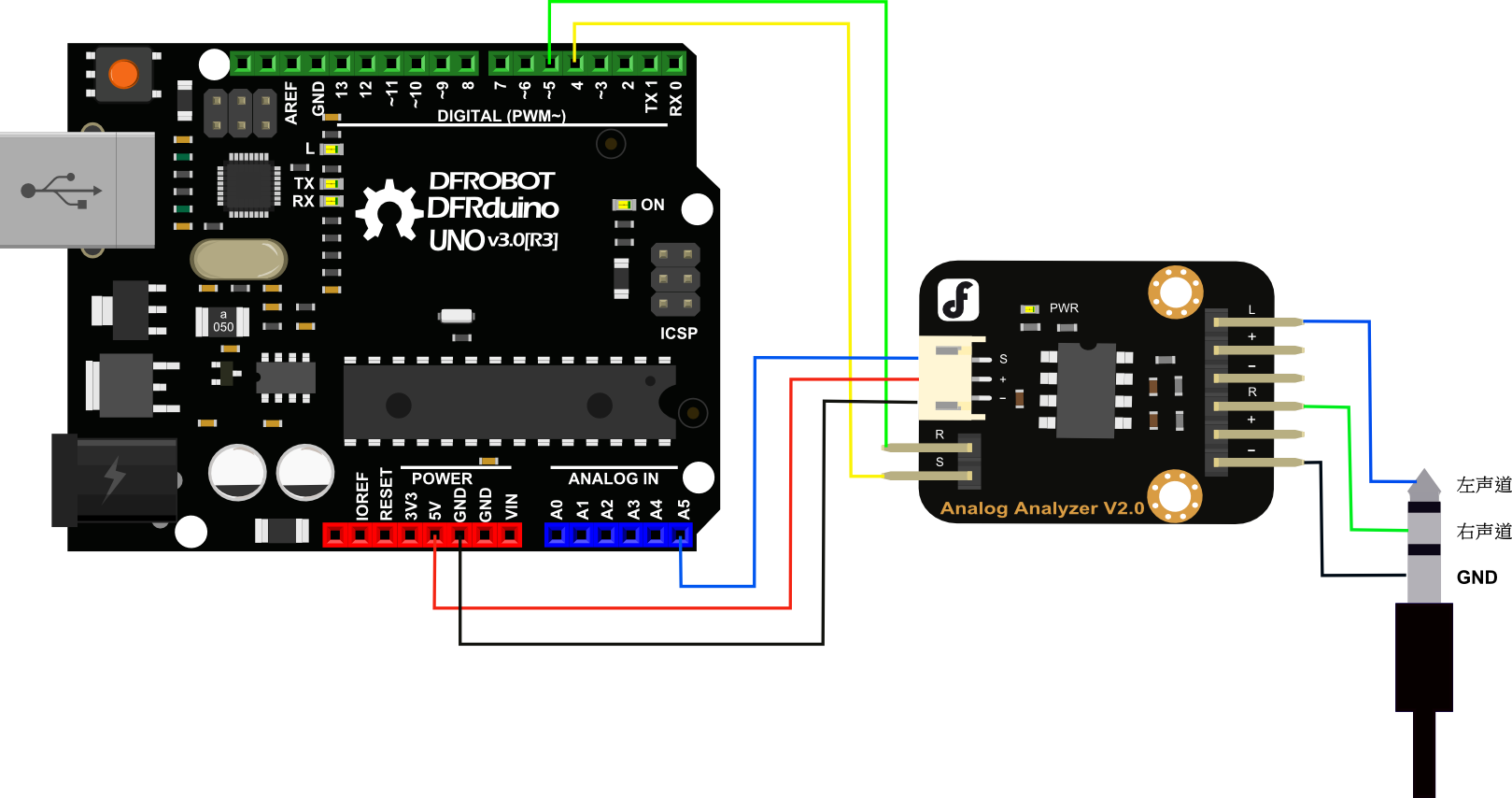
注意事项:可以和麦克风传感器(DFR0034)配套使用,完成与Arduino的音频采集。也可连接3.5mm音频信号接头作为信号输入。
应用领域
- 捕捉音乐频谱,制作音乐互动机器人
- 处理音频数据读取,制作灯光特效
- 语音分析
引脚说明

连线图
样例代码
Arduino IDE 样例代码
#include <AudioAnalyzer.h>
//Version 1.3 for Spectrum analyzer
//请下载最新的库文件
Analyzer Audio = Analyzer(4,5,5);//Strobe pin ->4 RST pin ->5 Analog Pin ->5
//Analyzer Audio = Analyzer();//Strobe->4 RST->5 Analog->0
int FreqVal[7];//
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(57600);
Audio.Init();//Init module
}
void loop()
{
Audio.ReadFreq(FreqVal);//返回7个带通滤波器过滤出的的7个对应值
//频率(Hz):63 160 400 1K 2.5K 6.25K 16K
//FreqVal[]: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
for(int i=0;i<7;i++)
{
Serial.print(max((FreqVal[i]-100),0));
if(i<6) Serial.print(",");
else Serial.println();
}
delay(20);
}
CVAVR 样例代码:
使用 atmega128 (clock 16Mhz), usart0 (波特率:9600), timer1 (scale clock 1024), adc. formula timer1 when use clock freq 16Mhz
Ttimer1 = Periode Timer1
TCNT1 = Register Timer1
N = Scale clock (1, 8, 64, 256 dan 1024)
Tosc = Periode clock
Fosc = Frekuensi clock cristal
Tosc = 1/Fosc
Tosc = 1/16Mhz = 0,0000000625
Ttimer1 = Tosc * (65536 - TCNT1) * N
1 (second) = 0,0000000625 * (65536 - TCNT1) * 1024
TCNT1 = 49911
TCNT1 = C2F7 (in hex) <-- 用于Timer 1溢出中断
Clock value = Fosc/N
Clock value = 16Mhz/1024 = 15,625 kHz <-- timer1 时钟频率
可以在程序中使用任一timer
/*****************************************************
Chip type : ATmega128
Program type : Application
Clock frequency : 16,000000 MHz
Memory model : Small
External SRAM size : 0
Data Stack size : 1024
*****************************************************/
int sec, band, freq[7], i;
unsigned long int time_a, time_b;
int stat = 0;
#include <mega128.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <delay.h>
// Timer 1 overflow interrupt service routine
interrupt [TIM1_OVF] void timer1_ovf_isr(void)
{
// Reinitialize Timer 1 value
TCNT1H=0xC2F7 >> 8;
TCNT1L=0xC2F7 & 0xff;
// Place your code here
sec++;
}
#define ADC_VREF_TYPE 0x40
// Read the AD conversion result
unsigned int read_adc(unsigned char adc_input)
{
ADMUX=adc_input | (ADC_VREF_TYPE & 0xff);
// Delay needed for the stabilization of the ADC input voltage
delay_us(10);
// Start the AD conversion
ADCSRA|=0x40;
// Wait for the AD conversion to complete
while ((ADCSRA & 0x10)==0);
ADCSRA|=0x10;
return ADCW;
}
void RstModule()
{
PORTD.0 = 0; //S Low
PORTD.1 = 1; //R High
PORTD.0 = 1; //S High
PORTD.0 = 0; //S Low
PORTD.1 = 0; //R Low
delay_us(72);
}
void Init()
{
DDRD.0 = 1; //S pin
DDRD.1 = 1; //R pin
RstModule();
}
void ReadFreq(int *value)
{
if (stat == 0) {
time_a = sec;
stat = 1;
} else if (stat == 1) {
time_b = sec;
if (time_b - time_a > 3) {
RstModule();
stat = 0;
}
}
for (band=0;band<7;band++) {
delay_us(10);
value[band] = read_adc(0);
delay_us(50);
PORTD.0 = 1; //S High
delay_us(18);
PORTD.0 = 0; //S Low
}
}
void main(void)
{
// Timer/Counter 1 initialization
// Clock source: System Clock
// Clock value: 15,625 kHz
// Mode: Normal top=FFFFh
// OC1A output: Discon.
// OC1B output: Discon.
// OC1C output: Discon.
// Noise Canceler: Off
// Input Capture on Falling Edge
// Timer 1 Overflow Interrupt: On
// Input Capture Interrupt: Off
// Compare A Match Interrupt: Off
// Compare B Match Interrupt: Off
// Compare C Match Interrupt: Off
TCCR1A=0x00;
TCCR1B=0x05;
TCNT1H=0xC2;
TCNT1L=0xF7;
ICR1H=0x00;
ICR1L=0x00;
OCR1AH=0x00;
OCR1AL=0x00;
OCR1BH=0x00;
OCR1BL=0x00;
OCR1CH=0x00;
OCR1CL=0x00;
// Timer(s)/Counter(s) Interrupt(s) initialization
TIMSK=0x04;
ETIMSK=0x00;
// USART0 initialization
// Communication Parameters: 8 Data, 1 Stop, No Parity
// USART0 Receiver: Off
// USART0 Transmitter: On
// USART0 Mode: Asynchronous
// USART0 Baud Rate: 9600
UCSR0A=0x00;
UCSR0B=0x08;
UCSR0C=0x06;
UBRR0H=0x00;
UBRR0L=0x67;
// Analog Comparator initialization
// Analog Comparator: Off
// Analog Comparator Input Capture by Timer/Counter 1: Off
ACSR=0x80;
SFIOR=0x00;
// ADC initialization
// ADC Clock frequency: 1000,000 kHz
// ADC Voltage Reference: AREF pin
ADMUX=ADC_VREF_TYPE & 0xff;
ADCSRA=0x84;
// Global enable interrupts
#asm("sei")
Init();
while (1)
{
ReadFreq(freq);
for (i=0;i<7;i++) {
printf("%d",freq[i]-100);
if(i<6) printf(", ");
else printf("\r\n");
}
delay_ms(20);
};
}
鸣谢: 该代码由论坛友人 Pandora 提供.
Mind+(基于Scratch3.0)图形化编程
1、下载及安装软件。下载地址:http://www.mindplus.cc 详细教程:
Mind+基础wiki教程-软件下载安装
2、切换到“上传模式”。 详细教程:
Mind+基础wiki教程-上传模式编程流程
3、“扩展”中选择“主控板”中的“Arduino Uno”,“功能模块”中加载“频谱分析模块”。 详细教程:Mind+基础wiki教程-加载扩展库流程
4、进行编程,程序如下图:
5、菜单“连接设备”,“上传到设备”
6、程序上传完毕后,打开串口即可看到数据输出。详细教程:
Mind+基础wiki教程-串口打印

结果
打开串口监视器,将波特率调整到9600,对模拟声音传感器发出响声,可以在串口中观察到数据随声音的增强而变大。
相关资料
 Go Shopping Audio Analyzer
Go Shopping Audio Analyzer