使用前请根据MicroPython使用教程烧录固件
1. 基础示例
通过基础示例可以快速的验证开发板板载功能是否正常。
1.1 录音
通过该示例可以验证开发板的MIC是否正常。该示例程序演示了通过MIC采集声音并保存到ESP32-P4上。
import os
from machine import Pin
from machine import I2S
SCK_PIN = 12
#WS_PIN = 25
SD_PIN = 9
I2S_ID = 0
BUFFER_LENGTH_IN_BYTES = 40000
# ======= AUDIO CONFIGURATION =======
WAV_FILE = "mic.wav"
RECORD_TIME_IN_SECONDS = 4
WAV_SAMPLE_SIZE_IN_BITS = 16
FORMAT = I2S.MONO
SAMPLE_RATE_IN_HZ = 4000
# ======= AUDIO CONFIGURATION =======
format_to_channels = {I2S.MONO: 1, I2S.STEREO: 2}
NUM_CHANNELS = format_to_channels[FORMAT]
WAV_SAMPLE_SIZE_IN_BYTES = WAV_SAMPLE_SIZE_IN_BITS // 8
RECORDING_SIZE_IN_BYTES = (
RECORD_TIME_IN_SECONDS * SAMPLE_RATE_IN_HZ * WAV_SAMPLE_SIZE_IN_BYTES * NUM_CHANNELS
)
def create_wav_header(sampleRate, bitsPerSample, num_channels, num_samples):
datasize = num_samples * num_channels * bitsPerSample // 8
o = bytes("RIFF", "ascii") # (4byte) Marks file as RIFF
o += (datasize + 36).to_bytes(
4, "little"
) # (4byte) File size in bytes excluding this and RIFF marker
o += bytes("WAVE", "ascii") # (4byte) File type
o += bytes("fmt ", "ascii") # (4byte) Format Chunk Marker
o += (16).to_bytes(4, "little") # (4byte) Length of above format data
o += (1).to_bytes(2, "little") # (2byte) Format type (1 - PCM)
o += (num_channels).to_bytes(2, "little") # (2byte)
o += (sampleRate).to_bytes(4, "little") # (4byte)
o += (sampleRate * num_channels * bitsPerSample // 8).to_bytes(4, "little") # (4byte)
o += (num_channels * bitsPerSample // 8).to_bytes(2, "little") # (2byte)
o += (bitsPerSample).to_bytes(2, "little") # (2byte)
o += bytes("data", "ascii") # (4byte) Data Chunk Marker
o += (datasize).to_bytes(4, "little") # (4byte) Data size in bytes
return o
audio_in = I2S(
I2S_ID,
sck=Pin(SCK_PIN),
#ws=Pin(WS_PIN),
sd=Pin(SD_PIN),
mode=I2S.PDM_RX,
bits=WAV_SAMPLE_SIZE_IN_BITS,
format=FORMAT,
rate=SAMPLE_RATE_IN_HZ * 4,
ibuf=BUFFER_LENGTH_IN_BYTES,
)
# allocate sample arrays
# memoryview used to reduce heap allocation in while loop
mic_samples = bytearray(40000)
mic_samples_mv = memoryview(mic_samples)
recording_buffer = bytearray(RECORDING_SIZE_IN_BYTES)
bytes_received = 0
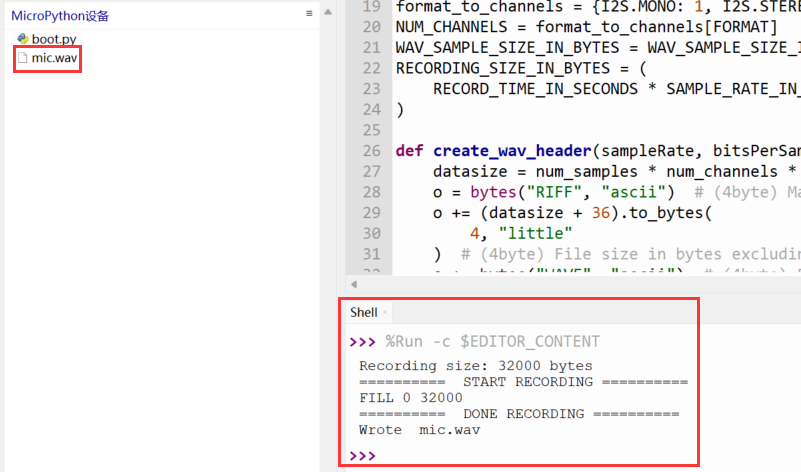
print("Recording size: {} bytes".format(RECORDING_SIZE_IN_BYTES))
print("========== START RECORDING ==========")
try:
while bytes_received < RECORDING_SIZE_IN_BYTES:
# read a block of samples from the I2S microphone
bytes_read = audio_in.readinto(mic_samples_mv)
if bytes_read > 0:
bytes_to_write = min(
bytes_read, RECORDING_SIZE_IN_BYTES - bytes_received
)
recording_buffer[bytes_received:bytes_received+bytes_to_write] = mic_samples_mv[0:bytes_to_write]
print('FILL', bytes_received, bytes_to_write)
bytes_received += bytes_read
print("========== DONE RECORDING ==========")
except (KeyboardInterrupt, Exception) as e:
print("caught exception {} {}".format(type(e).__name__, e))
# Write to WAV
wav = open(WAV_FILE, "wb")
# create header for WAV file and write to SD card
wav_header = create_wav_header(
SAMPLE_RATE_IN_HZ,
WAV_SAMPLE_SIZE_IN_BITS,
NUM_CHANNELS,
SAMPLE_RATE_IN_HZ * RECORD_TIME_IN_SECONDS,
)
wav.write(wav_header)
# write samples to WAV file
wav.write(recording_buffer)
# cleanup
wav.close()
print("Wrote ", WAV_FILE)
audio_in.deinit()
应用案例来自于:[Micropython]玩转ESP32P4:开启使用MicroPython
1.2 TF卡
通过该示例可以验证开发板的TF卡座子是否正常。该示例程序演示了读取TF卡的文件列表(使用前请插入TF卡到)。
from machine import Pin,SDCard
import os
sd = SDCard(slot=0,width=4, sck=43, cmd=44, data=(39, 40, 41, 42), freq=40000000)
os.mount(sd, '/sd')
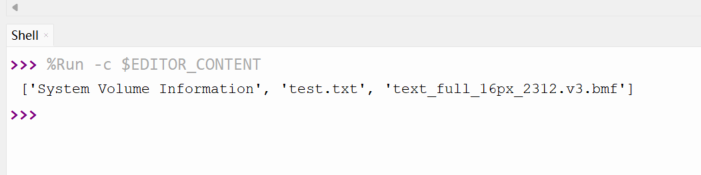
os.listdir('/sd')
print(os.listdir('/sd'))
os.listdir('/sd')
应用案例来自于:[Micropython]玩转ESP32P4:开启使用MicroPython
1.3 连接WiFi
通过该示例可以验证开发板的ESP32-C6无线通讯模组是否正常。该示例程序演示了通过ESP32-C6连接热点(使用前请修改第7行代码的SSIS和PWD)。
import network,time
def connect():
wlan = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
wlan.active(True)
if not wlan.isconnected():
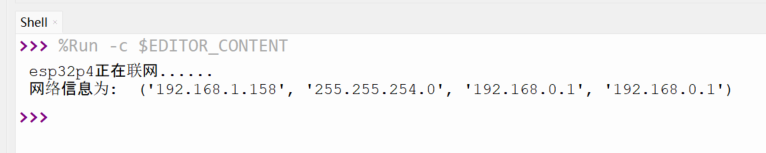
print('esp32p4正在联网',end="")
wlan.connect('SSID', 'PWD')
while not wlan.isconnected():
print(".",end="")
time.sleep(1)
print('\n网络信息为: ', wlan.ifconfig())
connect()
应用案例来自于:[Micropython]玩转ESP32P4:开启使用MicroPython
2. 应用示例
2.1 摄像头拍照
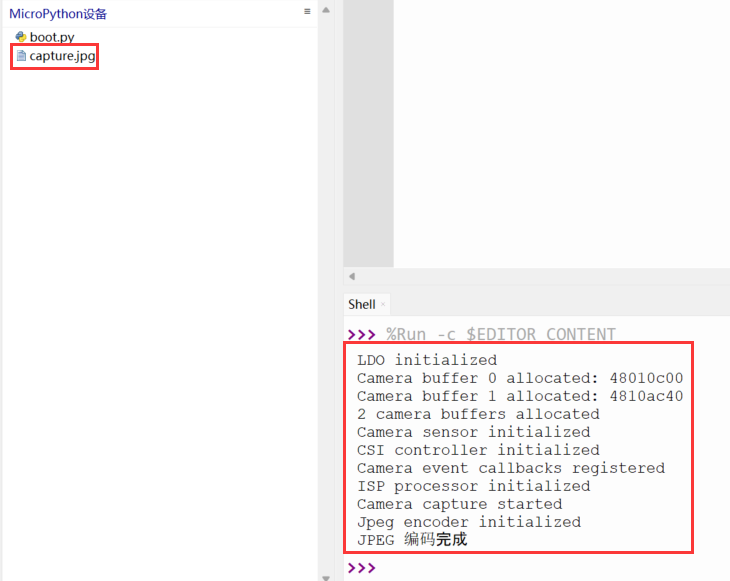
通过该示例演示了通过ESP32-P4进行拍照,并保存到设备。(使用前请连接摄像头)。
适配的摄像头:
-
SEN0173 树莓派摄像头模块 500万像素
import camera,time,jpeg
camera.init()
time.sleep(5)
img = camera.capture() # bytes
camera.deinit()
with open("capture.jpg", "wb") as f:
f.write(img)
print("JPEG 编码完成")
应用案例来自于:[Micropython]玩转ESP32P4:开启使用MicroPython
2.2 网页图传
该示例通过ESP32-P4创建一个网页服务器,可以通过浏览器查看摄像头的实时画面。
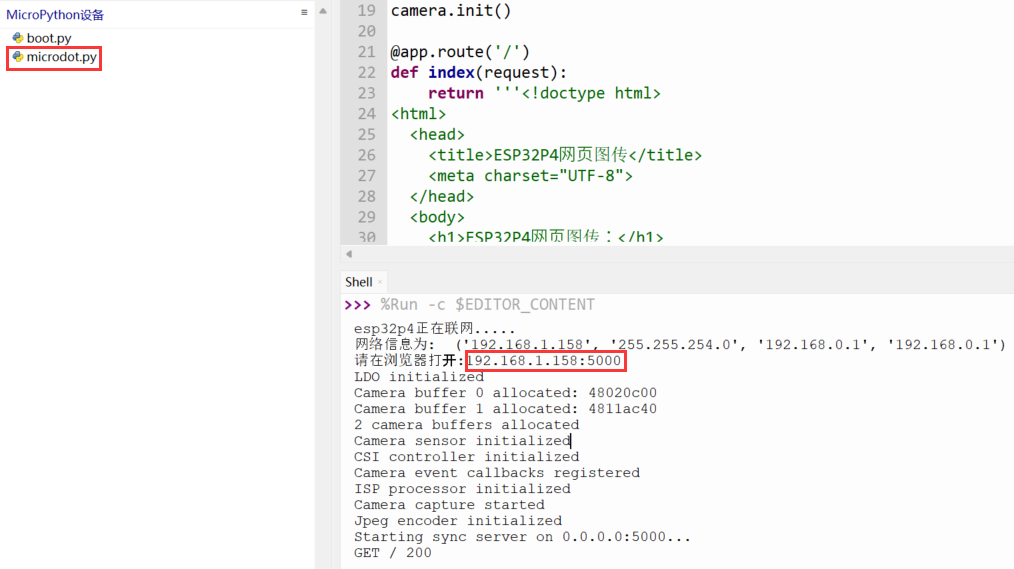
- 上传【microdot.py】文件到ESP32-P4
- 修改第9行代码的SSIS和PWD,并运行脚本
- 根据打印信息,通过浏览器访问IP地址即可访问网页(访问网页的设备和ESP32-P4须在同局域网)
from microdot import Microdot
import time,jpeg,camera,network
def connect():
wlan = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
wlan.active(True)
if not wlan.isconnected():
print('esp32p4正在联网',end="")
wlan.connect('ssid', 'PWD')
while not wlan.isconnected():
print(".",end="")
time.sleep(1)
print('\n网络信息为: ', wlan.ifconfig())
ifconfig = wlan.ifconfig()
print('请在浏览器打开:{}:5000'.format(ifconfig[0]))
connect()
app = Microdot()
camera.init()
@app.route('/')
def index(request):
return '''<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>ESP32P4网页图传</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<h1>ESP32P4网页图传:</h1>
<img src="/video_feed" width="50%">
</body>
</html>''', 200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8'}
@app.route('/video_feed')
def video_feed(request):
def stream():
yield b'--frame\r\n'
while True:
frame = camera.capture()
yield b'Content-Type: image/jpeg\r\n\r\n' + frame + \
b'\r\n--frame\r\n'
gc.collect()
#time.sleep_ms(50)
return stream(), 200, {'Content-Type':
'multipart/x-mixed-replace; boundary=frame'}
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
camera.deinit()
应用案例来自于:[Micropython]玩转ESP32P4:开启使用MicroPython
2.3 识别猫
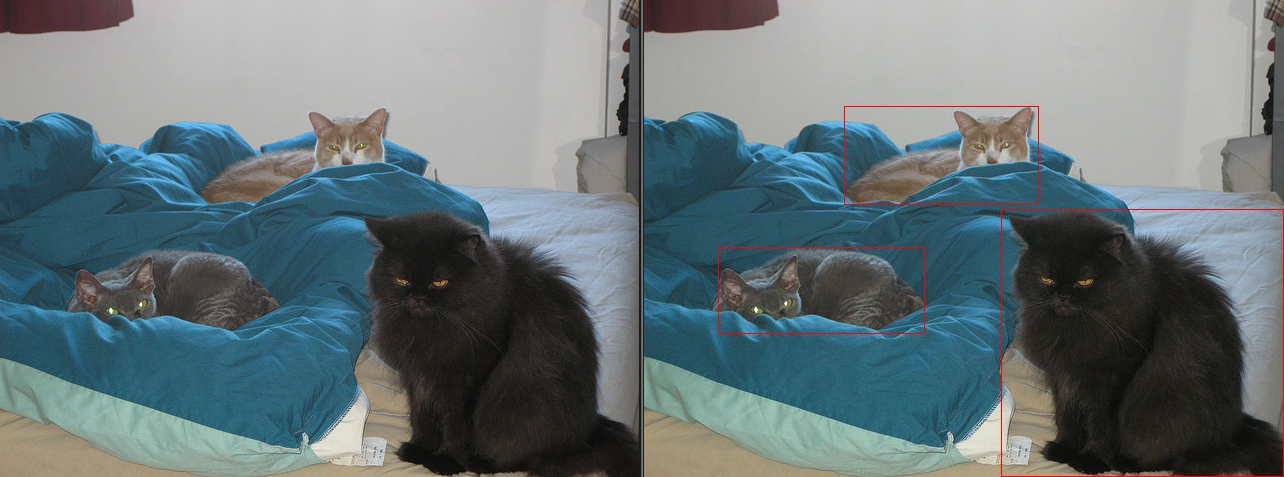
该示例演示了通过ESP32-P4识别图片中的猫,ESP32-P4将标注出图片中的猫并保存为新的图片。
- 上传【cat.jpg】文件到ESP32-P4
- 运行脚本即可看到位置信息
- 点击【停止/重启后端进程】按键即可看到MicroPython设备中标注的图片
from espdl import CatDetector
from jpeg import Decoder, Encoder
decoder = Decoder()
# 捕获并处理图像
img = open("cat.jpg", "rb").read() # 捕获原始图像(通常是JPEG格式)
wh = decoder.get_img_info(img)# 获取图像的宽度和高度
# 获取图像的宽度和高度
width, height = wh
encoder = Encoder(width=width, height=height, pixel_format="RGB888")
face_detector = CatDetector(width=width, height=height)
framebuffer = decoder.decode(img) # 转换为RGB888格式
# 将memoryview转换为bytearray以便修改
framebuffer = bytearray(framebuffer)
# 运行检测
results = face_detector.run(framebuffer)
# 绘制边框
def draw_rectangle(buffer, width, height, x, y, w, h, list1, color=(255, 0, 0)):
"""
在RGB888格式的图像缓冲区上绘制矩形边框
:param buffer: 图像缓冲区
:param width: 图像宽度
:param height: 图像高度
:param x: 边框左上角的x坐标
:param y: 边框左上角的y坐标
:param w: 边框宽度
:param h: 边框高度
:param color: 边框颜色(RGB格式)
"""
# 辅助函数:设置单个像素的颜色
def set_pixel(buffer, width, x, y, color):
offset = (y * width + x) * 3
buffer[offset] = color[0] # R
buffer[offset + 1] = color[1] # G
buffer[offset + 2] = color[2] # B
# 辅助函数:绘制更大的点
def draw_large_dot(buffer, width, x, y, color, size=3):
for i in range(x - size, x + size + 1):
for j in range(y - size, y + size + 1):
if 0 <= i < width and 0 <= j < height:
set_pixel(buffer, width, i, j, color)
# 绘制上边框
for i in range(x, x + w):
if 0 <= i < width and 0 <= y < height:
set_pixel(buffer, width, i, y, color)
# 绘制下边框
for i in range(x, x + w):
if 0 <= i < width and 0 <= y + h < height:
set_pixel(buffer, width, i, y + h, color)
# 绘制左边框
for j in range(y, y + h):
if 0 <= j < height and 0 <= x < width:
set_pixel(buffer, width, x, j, color)
# 绘制右边框
for j in range(y, y + h):
if 0 <= j < height and 0 <= x + w < width:
set_pixel(buffer, width, x + w, j, color)
# 绘制特征点
if list1:
draw_large_dot(buffer, width, list1[0], list1[1], (0, 0, 255), size=2)
draw_large_dot(buffer, width, list1[2], list1[3], (0, 0, 255), size=2)
draw_large_dot(buffer, width, list1[4], list1[5], (0, 255, 0), size=2)
draw_large_dot(buffer, width, list1[6], list1[7], (255, 0, 0), size=2)
draw_large_dot(buffer, width, list1[8], list1[9], (255, 0, 0), size=2)
if results:
# 在图像上绘制人脸边框
for face in results:
print(face)
x1, y1, x2, y2 = face['box']
draw_rectangle(framebuffer, width, height, x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1, None, color=(255, 0, 0)) # 使用红色边框
# 将带有边框的图像重新编码为JPEG格式并保存
marked_img = encoder.encode(framebuffer)
with open("cat_marked.jpg", "wb") as f:
f.write(marked_img)
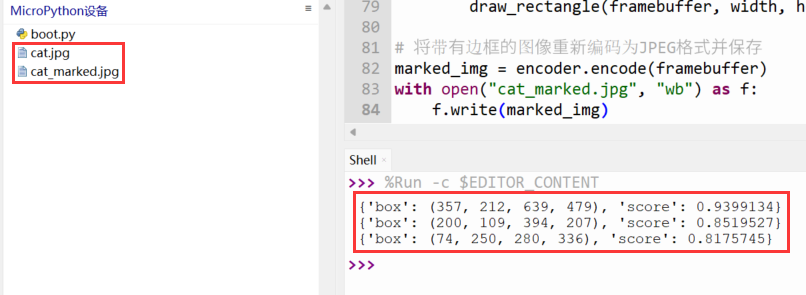
标注结果

应用案例来自于:[Micropython]Micropython玩转ESP32P4:绑定AI相关模块
2.4 识别人脸
该示例演示了通过ESP32-P4识别图片中的人脸,ESP32-P4将标注出图片中的人脸并保存为新的图片。
- 上传【face.jpg】文件到ESP32-P4
- 运行脚本即可看到位置信息
- 点击【停止/重启后端进程】按键即可看到MicroPython设备中标注的图片
from espdl import FaceDetector
from jpeg import Decoder, Encoder
decoder = Decoder()
encoder = Encoder(width=320, height=240, pixel_format="RGB888")
face_detector = FaceDetector()
# 捕获并处理图像
img = open("face.jpg", "rb").read() # 捕获原始图像(通常是JPEG格式)
framebuffer = decoder.decode(img) # 转换为RGB888格式
# 将memoryview转换为bytearray以便修改
framebuffer = bytearray(framebuffer)
# 运行人脸检测
results = face_detector.run(framebuffer)
# 绘制边框
def draw_rectangle(buffer, width, height, x, y, w, h, list1, color=(255, 0, 0)):
"""
在RGB888格式的图像缓冲区上绘制矩形边框
:param buffer: 图像缓冲区
:param width: 图像宽度
:param height: 图像高度
:param x: 边框左上角的x坐标
:param y: 边框左上角的y坐标
:param w: 边框宽度
:param h: 边框高度
:param color: 边框颜色(RGB格式)
"""
# 辅助函数:设置单个像素的颜色
def set_pixel(buffer, width, x, y, color):
offset = (y * width + x) * 3
buffer[offset] = color[0] # R
buffer[offset + 1] = color[1] # G
buffer[offset + 2] = color[2] # B
# 辅助函数:绘制更大的点
def draw_large_dot(buffer, width, x, y, color, size=3):
for i in range(x - size, x + size + 1):
for j in range(y - size, y + size + 1):
if 0 <= i < width and 0 <= j < height:
set_pixel(buffer, width, i, j, color)
# 绘制上边框
for i in range(x, x + w):
if 0 <= i < width and 0 <= y < height:
set_pixel(buffer, width, i, y, color)
# 绘制下边框
for i in range(x, x + w):
if 0 <= i < width and 0 <= y + h < height:
set_pixel(buffer, width, i, y + h, color)
# 绘制左边框
for j in range(y, y + h):
if 0 <= j < height and 0 <= x < width:
set_pixel(buffer, width, x, j, color)
# 绘制右边框
for j in range(y, y + h):
if 0 <= j < height and 0 <= x + w < width:
set_pixel(buffer, width, x + w, j, color)
# 绘制特征点
if list1:
draw_large_dot(buffer, width, list1[0], list1[1], (0, 0, 255), size=2)
draw_large_dot(buffer, width, list1[2], list1[3], (0, 0, 255), size=2)
draw_large_dot(buffer, width, list1[4], list1[5], (0, 255, 0), size=2)
draw_large_dot(buffer, width, list1[6], list1[7], (255, 0, 0), size=2)
draw_large_dot(buffer, width, list1[8], list1[9], (255, 0, 0), size=2)
# 在图像上绘制人脸边框
for face in results:
print(face)
x1, y1, x2, y2 = face['box']
draw_rectangle(framebuffer, 320, 240, x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1, face['features'], color=(255, 0, 0)) # 使用红色边框
# 将带有边框的图像重新编码为JPEG格式并保存
marked_img = encoder.encode(framebuffer)
with open("face_marked.jpg", "wb") as f:
f.write(marked_img)
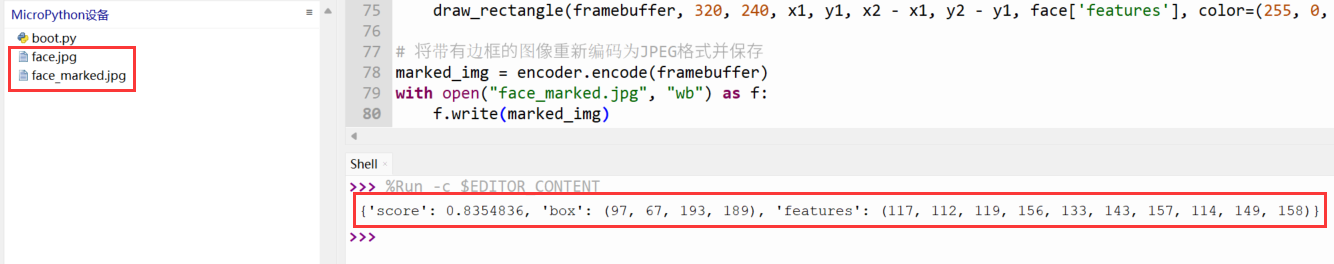
标注结果

应用案例来自于:[Micropython]Micropython玩转ESP32P4:绑定AI相关模块
2.5 行人检测
该示例演示了通过ESP32-P4识别图片中的行人,ESP32-P4将标注出图片中的行人并保存为新的图片。
- 上传【pedestrian.jpg】文件到ESP32-P4
- 运行脚本即可看到位置信息
- 点击【停止/重启后端进程】按键即可看到MicroPython设备中标注的图片
from espdl import HumanDetector
from jpeg import Decoder, Encoder
decoder = Decoder()
encoder = Encoder(width=640, height=480,pixel_format="RGB888")
human_detector = HumanDetector(width=640, height=480)
# 捕获并处理图像
img = open("pedestrian.jpg", "rb").read() # 捕获原始图像(通常是JPEG格式)
framebuffer = decoder.decode(img) # 转换为RGB888格式
# 将memoryview转换为bytearray以便修改
framebuffer = bytearray(framebuffer)
# 运行行人检测
results = human_detector.run(framebuffer)
# 绘制边框
def draw_rectangle(buffer, width, height, x, y, w, h, color=(255, 0, 0)):
"""
在RGB888格式的图像缓冲区上绘制矩形边框
:param buffer: 图像缓冲区
:param width: 图像宽度
:param height: 图像高度
:param x: 边框左上角的x坐标
:param y: 边框左上角的y坐标
:param w: 边框宽度
:param h: 边框高度
:param color: 边框颜色(RGB格式)
"""
# 辅助函数:设置单个像素的颜色
def set_pixel(buffer, width, x, y, color):
offset = (y * width + x) * 3
buffer[offset] = color[0] # R
buffer[offset + 1] = color[1] # G
buffer[offset + 2] = color[2] # B
# 绘制上边框
for i in range(x, x + w):
if 0 <= i < width and 0 <= y < height:
set_pixel(buffer, width, i, y, color)
# 绘制下边框
for i in range(x, x + w):
if 0 <= i < width and 0 <= y + h < height:
set_pixel(buffer, width, i, y + h, color)
# 绘制左边框
for j in range(y, y + h):
if 0 <= j < height and 0 <= x < width:
set_pixel(buffer, width, x, j, color)
# 绘制右边框
for j in range(y, y + h):
if 0 <= j < height and 0 <= x + w < width:
set_pixel(buffer, width, x + w, j, color)
# 在图像上绘制边框
for face in results:
print(face)
x1, y1, x2, y2 = face['box']
draw_rectangle(framebuffer, 640, 480, x1, y1, x2-x1, y2-y1, color=(255, 0, 0)) # 使用红色边框
# 将带有边框的图像重新编码为JPEG格式并保存
marked_img = encoder.encode(framebuffer)
with open("pedestrian_marked.jpg", "wb") as f:
f.write(marked_img)
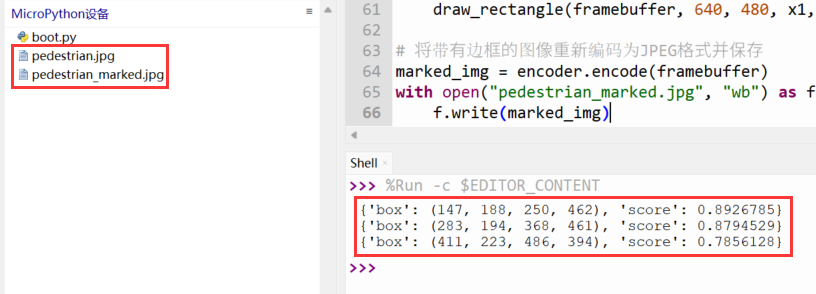
标注结果

应用案例来自于:[Micropython]Micropython玩转ESP32P4:绑定AI相关模块
2.6 yolo11
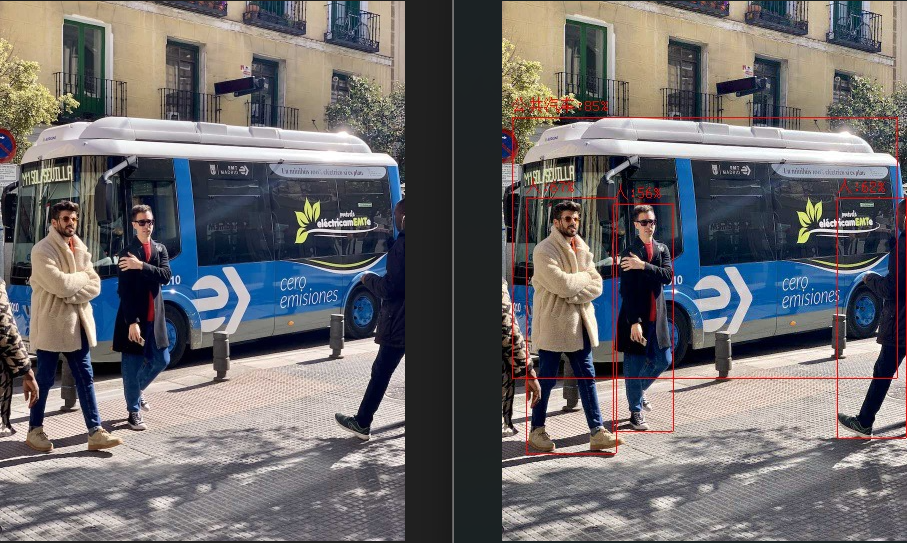
该示例演示了通过ESP32-P4对图片中物体进行分类,ESP32-P4将标注出图片中的物体信息并保存为新的图片。
- 上传【yolo.jpg】和【myufont.py】文件到ESP32-P4
- 运行脚本即可看到位置信息
- 点击【停止/重启后端进程】按键即可看到MicroPython设备中标注的图片
from espdl import CocoDetector
from jpeg import Decoder, Encoder
from myufont import CustomBMFont
from machine import Pin,SDCard
import os
sd = SDCard(slot=0,width=4, sck=43, cmd=44, data=(39, 40, 41, 42))
os.mount(sd, '/sd')
decoder = Decoder()
encoder = Encoder(width=405, height=540,pixel_format="RGB888")
face_detector = CocoDetector(width=405, height=540)
MSCOCO_CLASSES = [
"人", "自行车", "汽车", "摩托车", "飞机", "公共汽车", "火车", "卡车", "船", "交通灯",
"消防栓", "消防水带", "停车计时器", "长椅", "鸟", "猫", "狗", "马", "羊", "牛",
"大象", "熊", "斑马", "长颈鹿", "背包", "伞", "手提包", "领带", "行李箱", "飞盘",
"滑雪板", "滑雪杖", "滑板", "冲浪板", "网球拍", "瓶子", "酒杯", "杯子", "刀叉", "碗",
"香蕉", "苹果", "三明治", "橙子", "西兰花", "胡萝卜", "热狗", "披萨", "甜甜圈", "蛋糕",
"椅子", "沙发", "盆栽", "床", "餐桌", "马桶", "电视", "笔记本电脑", "鼠标", "遥控器",
"键盘", "手机", "微波炉", "烤箱", "烤面包机", "水槽", "冰箱", "书", "时钟", "花瓶",
"剪刀", "泰迪熊", "吹风机", "牙刷"
]
font = CustomBMFont('/sd/text_full_16px_2312.v3.bmf')
# 捕获并处理图像
img = open("yolo.jpg", "rb").read() # 捕获原始图像(通常是JPEG格式)
framebuffer = decoder.decode(img) # 转换为RGB888格式
# 将memoryview转换为bytearray以便修改
framebuffer = bytearray(framebuffer)
# 运行人脸检测
results = face_detector.run(framebuffer)
# 绘制边框
def draw_rectangle(buffer, width, height, x, y, w, h,font,label, color=(255, 0, 0)):
"""
在RGB888格式的图像缓冲区上绘制矩形边框
:param buffer: 图像缓冲区
:param width: 图像宽度
:param height: 图像高度
:param x: 边框左上角的x坐标
:param y: 边框左上角的y坐标
:param w: 边框宽度
:param h: 边框高度
:param color: 边框颜色(RGB格式)
"""
# 辅助函数:设置单个像素的颜色
def set_pixel(buffer, width, x, y, color):
offset = (y * width + x) * 3
buffer[offset] = color[0] # R
buffer[offset + 1] = color[1] # G
buffer[offset + 2] = color[2] # B
def is_chinese(ch):
"""判断一个字符是否为中文字符"""
if '\u4e00' <= ch <= '\u9fff' or \
'\u3400' <= ch <= '\u4dbf' or \
'\u20000' <= ch <= '\u2a6df':
return True
return False
def text(font, text, x_start, y_start, color,spacing=0, line_spacing=0, max_width=width):
font_size = font.font_size
bytes_per_row = (font_size + 7) // 8 # 每行占用的字节数
x, y = x_start, y_start
for char in text:
# 处理换行符
if char == '\n':
y += font_size + line_spacing
x = x_start
continue
if char == '\r':
x += 2*font_size
continue
# 获取字符宽度(中文字符全宽,ASCII字符半宽)
char_width = font_size if is_chinese(char) else font_size // 2
# 检查是否需要换行
if max_width is not None and x + char_width > x_start + max_width:
y += font_size + line_spacing
x = x_start
# 获取字符位图
bitmap = font.get_char_bitmap(char)
# 绘制字符
for row in range(font_size):
for col in range(char_width if not is_chinese(char) else font_size):
byte_idx = row * bytes_per_row + col // 8
bit_mask = 0x80 >> (col % 8)
if byte_idx < len(bitmap) and (bitmap[byte_idx] & bit_mask):
set_pixel(framebuffer,max_width,x + col, y + row, color)
# 移动到下一个字符位置
x += char_width + spacing
# 绘制上边框
for i in range(x, x + w):
if 0 <= i < width and 0 <= y < height:
set_pixel(buffer, width, i, y, color)
# 绘制下边框
for i in range(x, x + w):
if 0 <= i < width and 0 <= y + h < height:
set_pixel(buffer, width, i, y + h, color)
# 绘制左边框
for j in range(y, y + h):
if 0 <= j < height and 0 <= x < width:
set_pixel(buffer, width, x, j, color)
# 绘制右边框
for j in range(y, y + h):
if 0 <= j < height and 0 <= x + w < width:
set_pixel(buffer, width, x + w, j, color)
text(font,label, x, y-20, color)
# 在图像上绘制人脸边框
for face in results:
#print(face)
x1, y1, x2, y2 = face['box']
label = MSCOCO_CLASSES[face['category']]+":"+str(int(face['score']*100))+"%"
draw_rectangle(framebuffer, 405, 540, x1, y1, x2-x1, y2-y1,font,label) # 使用红色边框
print(label)
# 将带有边框的图像重新编码为JPEG格式并保存
marked_img = encoder.encode(framebuffer)
with open("yolo_marked.jpg", "wb") as f:
f.write(marked_img)
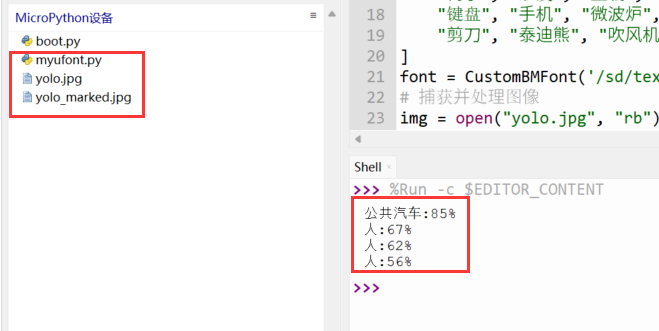
标注结果

应用案例来自于:[Micropython]Micropython玩转ESP32P4:绑定AI相关模块
2.7 MQTT上报数据
该示例演示了ESP32-P4通过MQTT协议上报数据到网络(使用前请修改11-20行代码信息)。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# main.py
import json
import network
import time
import random
from machine import ADC, Pin
from umqtt.simple import MQTTClient
# ========== 用户可改区域 ==========
WIFI_SSID = "xxx"
WIFI_PASS = "xxx"
ADC_PIN = 16 # ESP32-P4 的 ADC0 引脚
MQTT_SERVER = "192.168.31.160"
MQTT_PORT = 32768
MQTT_CLIENT_ID = 'micropython-client-{id}'.format(id=random.getrandbits(8))
MQTT_USER = "xxx"
MQTT_PASS = "xxx"
PUB_TOPIC = "esp/adc/temp"
PUB_INTERVAL = 2 # 发布间隔(秒)
# ===================================
def wifi_connect(ssid, pwd):
sta = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
sta.active(True)
if not sta.isconnected():
print("Connecting Wi-Fi...")
sta.connect(ssid, pwd)
for _ in range(20):
if sta.isconnected():
break
time.sleep(1)
print("Wi-Fi connected:", sta.ifconfig())
# --------------- 温度转换 ---------------
def read_temperature():
"""
线性转换:
参考电压 3.3 V,温度传感器输出 10 mV/°C
"""
adc = ADC(Pin(ADC_PIN))
adc.atten(ADC.ATTN_11DB) # 0-3.3 V
raw = adc.read()
volt = raw / 4095 * 3.3 # ADC 电压
temp = (volt - 1.4) * 100 # ADC 温度
return round(temp, 1)
# --------------- MQTT 连接 ---------------
def mqtt_connect():
c = MQTTClient(MQTT_CLIENT_ID, MQTT_SERVER, MQTT_PORT,
MQTT_USER, MQTT_PASS)
c.connect()
print("[MQTT] Connected to", MQTT_SERVER)
return c
def mqtt_publish(client, data: dict):
payload = json.dumps(data)
client.publish(PUB_TOPIC, payload)
print("[MQTT] Sent ->", payload)
# --------------- 主函数 ---------------
def main():
wifi_connect(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PASS) # 连接 WiFi
client = mqtt_connect()
while True:
temp = read_temperature()
mqtt_publish(client, {"temperature": temp})
time.sleep(PUB_INTERVAL)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()